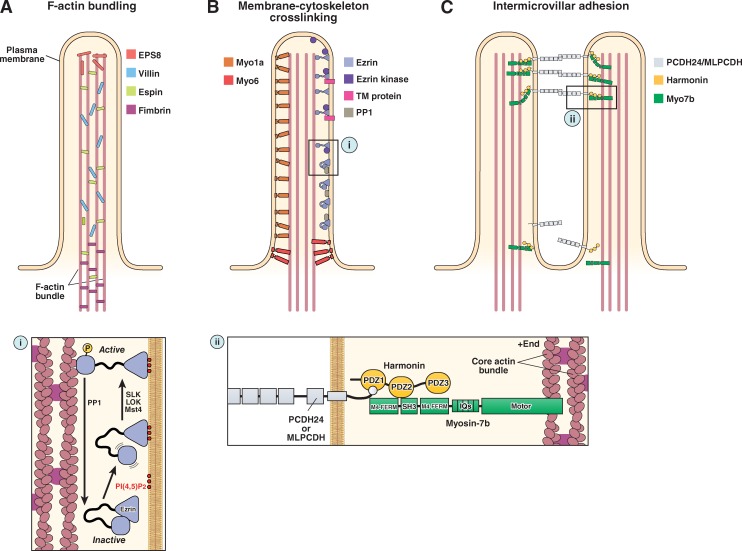
Figure 3.
The molecular machinery of microvillar protrusion, stabilization, and organization. (A) Bundling of actin filaments in the microvillar actin core is performed through the collective and potentially redundant function of villin, espin, fimbrin, and EPS8. (B) Membrane–cytoskeleton cross-linking plays an important role in microvillar stabilization and is mediated by myo1a, myo6, and the active form of ezrin (i). (C) Extracellular adhesion between the distal tips of microvilli (i.e., intermicrovillar adhesion) is used to optimize the packing of these protrusions during brush border assembly. Intermicrovillar adhesion is mediated by a trans-heterophilic complex of PCDH24 and MLPCDH. Distal tip targeting of microvillar protocadherins requires interactions with harmonin and, potentially, myosin-7b (ii). See main text for details on the function of the other proteins depicted in the figure.