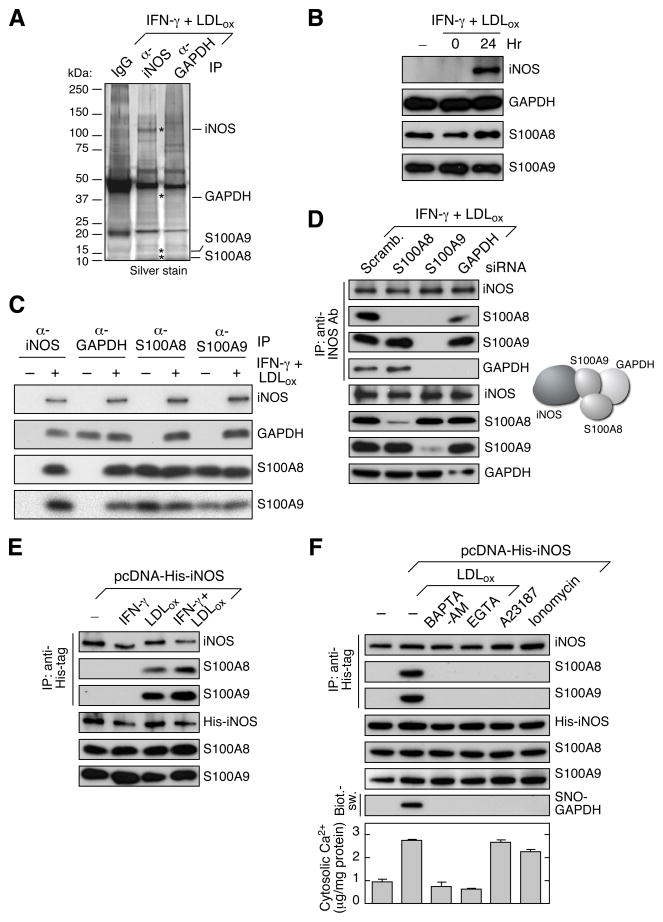
Figure 2. S100A8/A9 Directs iNOS-GAPDH Interaction and GAPDH S-Nitrosylation.
(A) S100A8 and S100A9 identified as binding partners of iNOS and GAPDH. PBM were incubated for 24 hr with LDLox/IFN-γ. Lysates were subjected to IP with anti-iNOS or anti-GAPDH antibodies, or control IgG, and analyzed by electrophoresis and silver stain. Specific bands were identified by LC-MS analysis.
(B) LDLox/IFN-γ does not induce S100A8 or S100A9 expression. Lysates from treated PBM were subjected to IB analysis with antibodies indicated.
(C) LDLox/IFN-γ induces assembly of iNOS-S100A8/A9-GAPDH complex. Lysates from treated PBM were subjected to IP and IB analysis with antibodies indicated.
(D) S100A9 facilitates binding of S100A8 and GAPDH to iNOS. PBM were transfected with siRNA targeting S100A8, S100A9, or GAPDH. After LDLox/IFN-γ treatment, lysates from treated cells were IP with anti-iNOS antibody and subjected to IB with antibodies indicated (left). Protein interaction model is shown (right).
(E) LDLox induces binding of S100A8 and S100A9 to iNOS. PBM were transfected with His-iNOS. After recovery, cells were treated with IFN-γ, LDLox, or both; lysates from treated PBM were subjected to IP and IB analysis with antibodies indicated.
(F) LDLox-stimulated intracellular Ca2+ is required for iNOS-S100A8/A9 complex assembly and activity. PBM that ectopically expressed His-iNOS were treated with LDLox in the presence of calcium chelators 15 μM BAPTA-AM or 2 mM EGTA, or with calcium ionophores 5 μM A23187 or 1 μM ionomycin. Lysates were subject to IP and IB with indicated antibodies or Biot.-sw. analysis. Cytosolic calcium was determined with o-cresolphthalein at 575 nm, and normalized to total cytosolic protein (mean ± SEM, n = 5 experiments).
See also Figure S1.