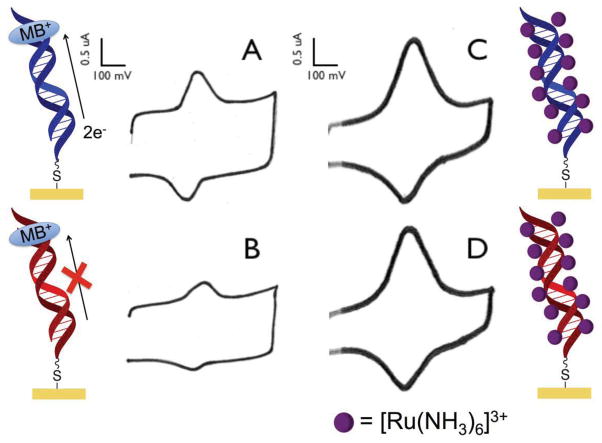
Figure 2.
Response of MB and [Ru(NH3)6]3+ on DNA-modified electrodes. MB is capable of intercalation into DNA, resulting in a DNA-mediated signal. In contrast, Ru(NH3)63+ interacts electrostatically with DNA, which merely reports on the number of anionic phosphates, not on the integrity of the DNA. (a) Cyclic voltammogram obtained from free MB interacting with a Watson-Crick paired DNA monolayer. (b) The incorporation of a single-base mismatch into the DNA assembled on the electrode significantly attenuates the signal obtained from the MB reporter. (c) Cyclic voltammogram obtained from the interaction between Ru(NH3)63+ and a DNA-modified electrode. (d) Upon incorporation of a single-base mismatch, no signal loss is observed with the Ru(NH3)63+ reporter. Only electrochemical reporters that interact with the DNA base stack report on DNA-mediated CT.