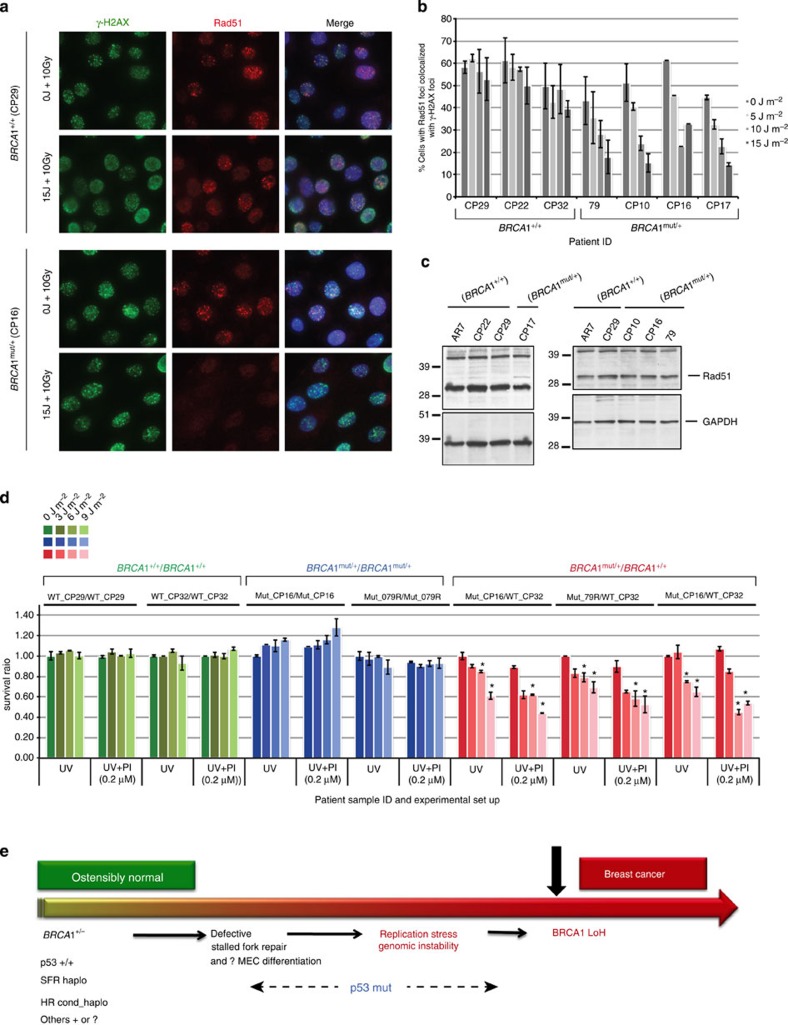
Figure 6. Evidence of conditional haploinsufficiency for DSBR in BRCA1mut/+ HMECs after pre-exposure to a stalled fork- inducing agent.
(a) Recruitment of Rad51 to IR-induced DSBs is reduced in heterozygous BRCA1mut/+, and not in WT BRCA1+/+ HMECs, when pre-exposed to stalled fork-inducing damage. HMECs derived from a BRCA1 mutation carrier (CP16, BRCA1mut/+) and a wt counterpart (CP29, BRCA1+/+) were irradiated with different doses of UV (5, 10 or 15 J m−2) and allowed to recover for 1 h. Cells were then irradiated with IR (10 Gy) and fixed 4 h post IR. Fixed cells were coimmunostained with Abs to γ-H2AX and Rad51. Additional wt and heterozygous strains were also assayed (in panel b). (b) Additional BRCA1+/+ and BRCA1mut/+ strains were analysed as described in (a). A graph depicting the fraction of cells in each additional HMEC strain that contains Rad51 foci after exposure to increasing doses of UV followed by 10 Gy dose of IR was plotted. The mean results and s.d. of data from at least three experiments are shown for each line. (c) Rad51 expression in BRCA1mut/+ and BRCA1+/+ HMEC lines. Whole-cell extracts from various BRCA1mut/+ and BRCA1+/+ strains were analysed by western blot. GAPDH was used as a loading control in these blots. (d) Combinations of BRCA1mut/+ and BRCA1+/+ HMECs (green: BRCA1+/+/BRCA1+/+, blue: BRCA1mut/+/ BRCA1mut/+ and red: BRCA1mut/+/BRCA1+/+) were irradiated with different doses of UV (0, 3, 6 and 9 J m−2), allowed to recover for 1 h, and then treated with either 0.2 μM PARP inhibitor (PI=olaparib; UV+PI) or DMSO as control (UV). Cells were grown for five more days before harvesting for FACS analysis. Data are plotted for the three, different cell combinations, and the error bars were calculated as the standard error propagation (SEP) in the ratios of each of the combinations in three, independent experiments. Data marked with an asterisk (*) reveal statistically significant differences (P-value<0.05) between UV and UV+PI sets. (e) One Possible Model of BRCA1 mutation- driven tumorigenesis. This model speculates that certain abnormal developments might occur during the extended period between full mammary development and the appearance of a BRCA1 breast cancer.