Figure 7.
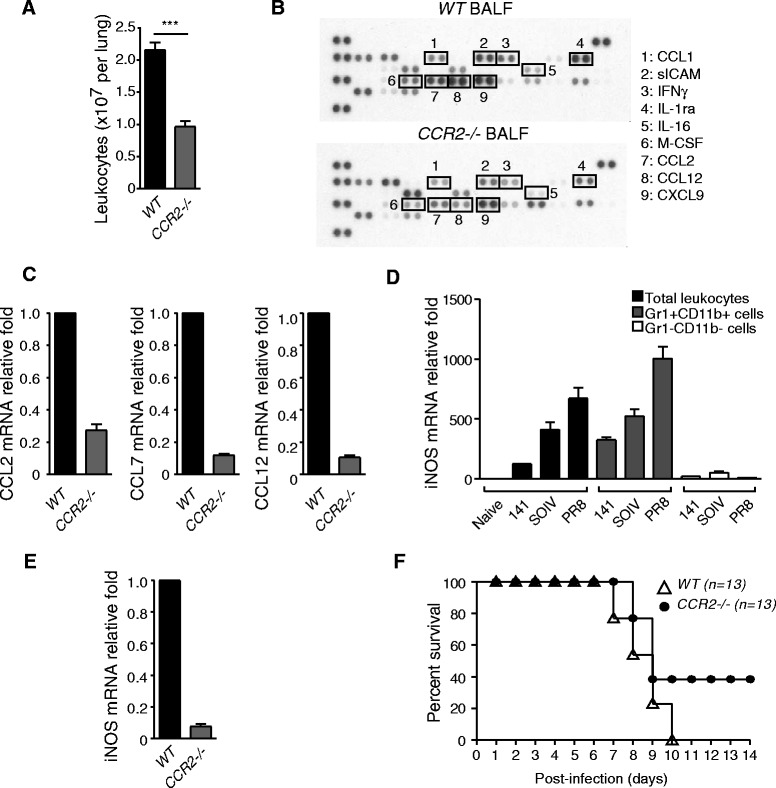
Decreasing pathological effects in PR8-infected CCR2 −/− mice. (A) Total leukocytes were harvested from the lungs and counted by trypan blue exclusion. These data are a composite of three independent experiments (n = 9 mice per group, mean ± SEM; ***P < 0.001). (B) Pooled BALFs were subjected to cytokine or chemokine expression analysis using cytokine protein arrays (n = 6 mice per group). (C) Relative expression of CCL2, CCL7 and CCL12 was measured by RT-QPCR. The mRNA relative folds were determined by normalizing the level of each group to the corresponding GADPH level and then to total leukocytes from WT mice (mean ± SEM). This is a representative result from two repeated experiments. (D) RNAs were extracted from total leukocytes, Gr1+ CD11b+ sorted cells and Gr1-CD11b- sorted cells from the virus-infected mice indicated. Relative expression of iNOS transcripts was measured by RT-QPCR. The mRNA relative folds were determined by normalizing the level of each group to the corresponding GAPDH level and then to total leukocytes from naïve mice (mean ± SEM). Experiment (n = 3–6 mice per group) was performed twice and one representative is shown. (E) RNAs were harvested from leukocytes isolated from the lungs of WT and CCR2−/− infected mice. Relative expression of iNOS was measured by RT-QPCR. The mRNA relative folds were determined by normalizing the level of each group to the corresponding GAPDH level and then to total leukocytes from WT mice (n = 3 mice per group; mean ± SEM). Experiment was performed twice and one representative is shown. (F) WT (n = 13) and CCR2−/− mice (n = 13) were infected with PR8 viruses. Survival rate was monitored daily until day 14 post-infection. These data are a composite of three independent experiments.
