Figure 1.
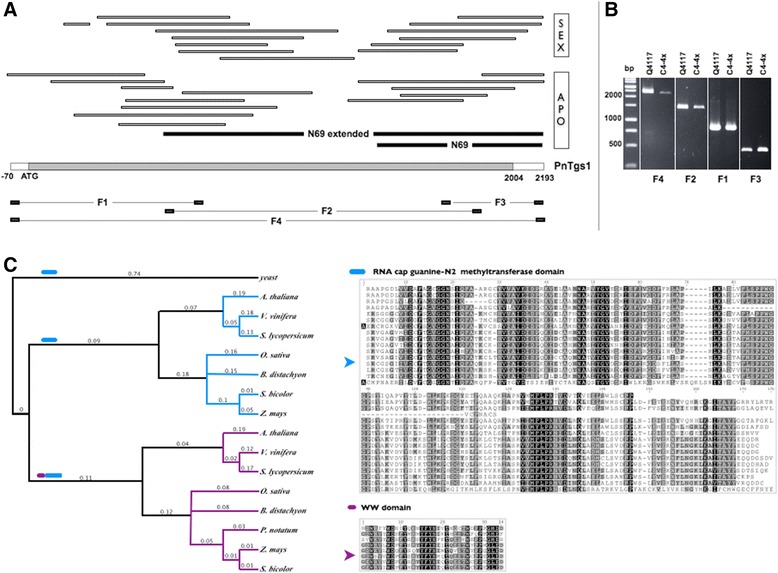
N69 partial cDNA derives from a plant-specific gene encoding a trimethyl guanosine synthase. (A) A consensus cDNA sequence was assembled using N69 cDNA, a N69-extended fragment obtained by RACE (black bars) and reads from RNA 454 sequencing in sexual (C4-4x) and apomictic (Q4117) reproductive tissues (white bars). This sequence contains a 2004 bp predicted ORF coding for a product sharing homology with yeast TRIMETHYL GUANOSINE SYNTHASE 1 (TGS1). (B) Primers were designed in order to amplify 4 different sequence fragments (F1, F2, F3, F4), which were amplified and sequenced for validation, from reproductive tissues of apomictic (Q4117) and sexual (C4-4x) genotypes. (C) Phylogenetic analysis of proteins similar to yeast TGS1 from several yeast and plant model species revealed that the Paspalum notatum predicted product is highly similar with plant specific members of the TGS1 protein family defined by the association of the RNA-cap guanine-N2 methyltransferase domain with a WW domain. Domains are indicated as colored ticks. ClustalW alignments are shown on the right (arrows indicate Pasalum notatum sequences).
