FIGURE 2.
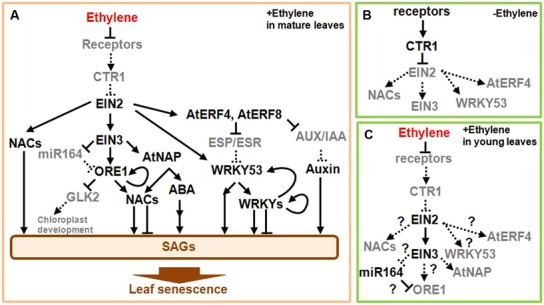
Scheme of the ethylene signaling pathway leading to the onset of leaf senescence. (A) In mature leaves, the detection of ethylene activates the downstream signaling pathway leading to SAG induction and leaf senescence. (B) In young and mature leaves, the receptors constitutively repress the downstream signaling in the absence of ethylene. (C) In young leaves, the detection of ethylene activates the downstream signaling pathway, but does not itself induce leaf senescence. Note that EIN2 and EIN3 are active and induce some ethylene responses, but not leaf senescence by an uncharacterized mechanism, in which some regulators of leaf development are likely involved. Arrows and bars at the end of each line show positive and negative regulations, respectively. Solid lines and black gene names designate the active form, while dotted lines and gray gene names indicate the inactive form. Several transcription factors (TFs) and signals such as jasmonic acid are not drawn in this scheme owing to space limitations. A detailed description on the scheme is presented in the main text.
