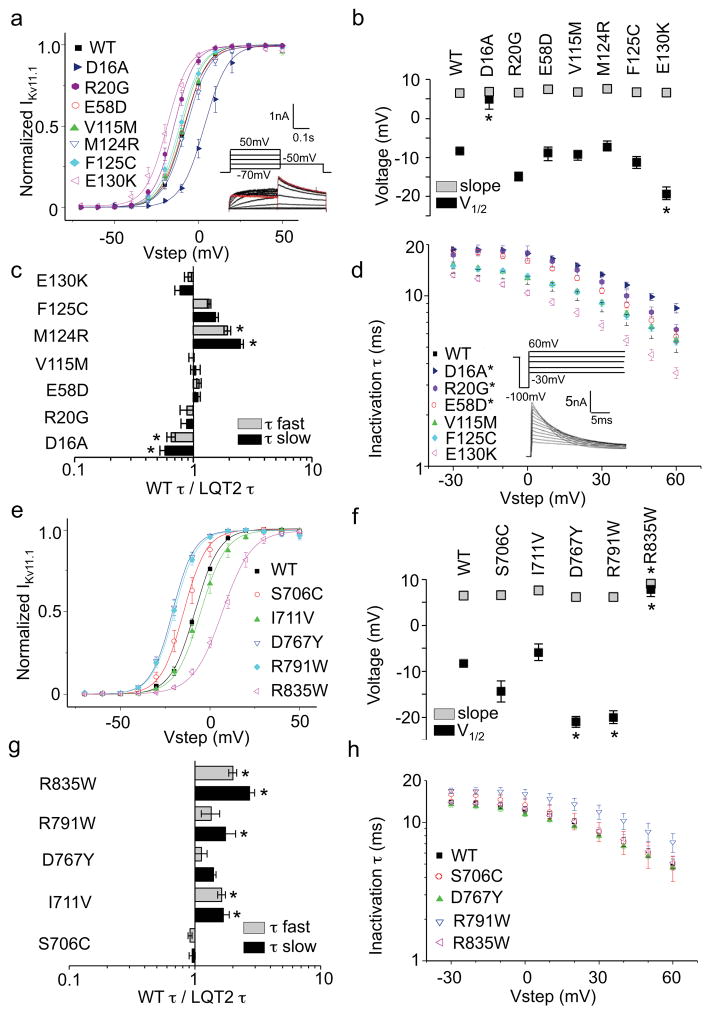
Figure 3. Electrophysiological properties of LQT2-linked EAGD and C-linker/CNBHD missense mutations.
(a, e) Activation current-voltage (I-V) relationships. From a holding potential of −80mV, cells were depolarized to voltages between −70mV and 50mV in 10mV increments for 3s to quantify tail current. I-V relations were determined by normalizing peak tail currents (Itail) from each step to the maximal peak Itail. (b, f) V1/2 and slope factors. The voltage at which peak IKv11.1 was half-maximal (V1/2) and the slope factor (k) were determined by fitting the normalized I-V relationship with the Boltzmann function. (c, g) WT-to-mutant time constant ratios (speeding factor) for deactivation at −50mV. The fast (taufast) and slow (tauslow) time constants of channel deactivation were determined with a double exponential fit of the Itail decay from 50mV to −50mV (red trace).. (d, h) Inactivation time constants determined at 0mV. From a holding potential of −80mV, cells were depolarized to 50mV for 1.5s to open and inactivate channels followed by a short 10ms step to −100mV to remove inactivation without allowing enough time for the channels to deactivate. This was followed by test pulses from −30mV to 60mV in 10mv increments. Inactivation time constants for each step were fit with a single exponential. Error bars are SEM. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (p<0.05). n = 3 to 9 HEK293 cells for each experiment.