Figure 1.
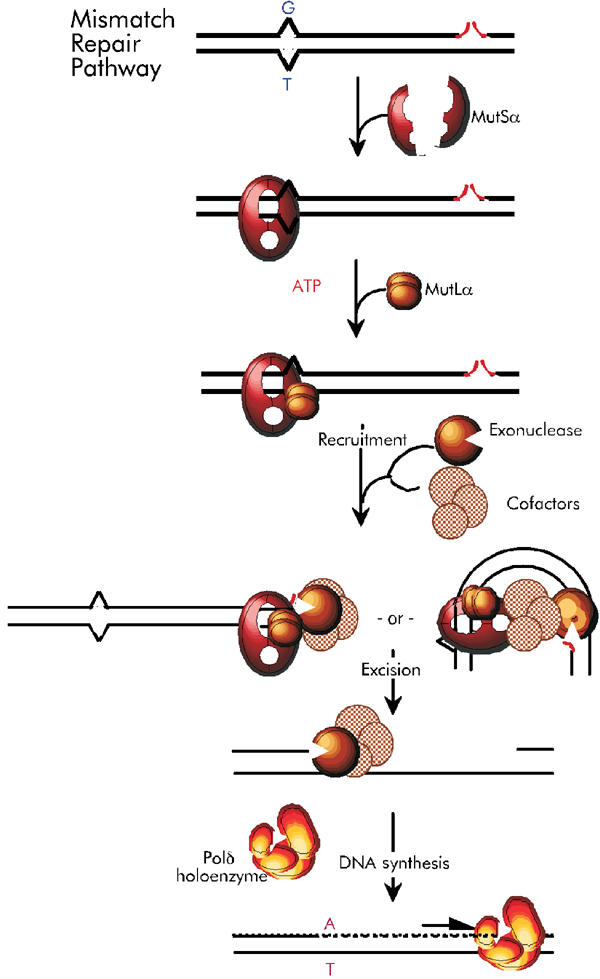
Alternative mismatch-correction pathways. Mismatches (G/T) are bound by MutSα heterodimers (red) and MutLα (bronze), in the presence of ATP, forming recognition complexes. Possible recognition-complex accessory proteins, such as PCNA, are not shown. Mismatch recognition is coupled to identification of the excision-initiation nick, concomitant with recruitment of exonuclease(s) (bronze) and (a) excision co-factor(s), for example, helicases (pink), via recognition-complex sliding (left) or contact of mismatch-bound recognition complexes with nicks or nick-associated proteins, by DNA bending (right). Excision proceeds from nicks to approximately 0.15 kbp past the mismatch, and DNA synthesis restores homoduplex (A/T) DNA.
