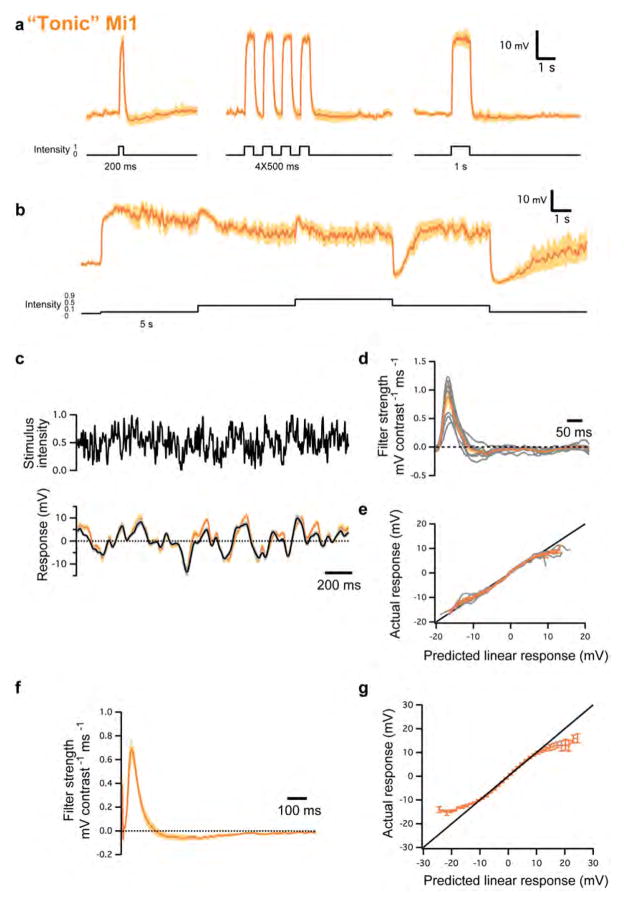
Extended Data Figure 9. Evoked response of ‘tonic’ Mi1 neurons.
a, Average evoked responses (± s.e.m.) of ‘tonic’ Mi1 (n =9) in response to 200 ms, four consecutive 250 ms and 1 s full-field flashes of light from dark. b, Average evoked responses (± s.e.m.) of ‘tonic’ Mi1 (n =7) in response to 5 s steps of light. c, Top: 2 s excerpt of the intensity signal from the 10 s full-field Gaussian noise stimulus. Correlation time is 10 ms. Bottom: average voltage response (± s.e.m.) of ‘tonic’ Mi1 (n =8) in response to the 2 s noise stimulus on top. The black trace corresponds to the average predicted linear response obtained by convolving the stimulus with the filters in d (± s.e.m.). d, Average temporal filters (± s.e.m.) extracted from the data in c that best predict the measured response of ‘tonic’ Mi1 as a function of contrast history. Individual filters are shown in grey. e, Nonlinearities for ‘tonic’ Mi1 cells. Actual responses are plotted against their linear predicted responses. Individual cell nonlinearities in grey; mean and s.e.m. are represented by the coloured line and patch. A line of slope 1 is shown in black. f, Average temporal filters (± s.e.m.) extracted from the highest-responding pixels for each ‘tonic’ Mi1 neuron in the spatio-temporal experiments. g, Averaged actual responses of ‘tonic’ Mi1 plotted against their averaged linear predicted responses in the spatio-temporal experiments. Error bars, s.e.m. A line of slope 1 is shown in black.