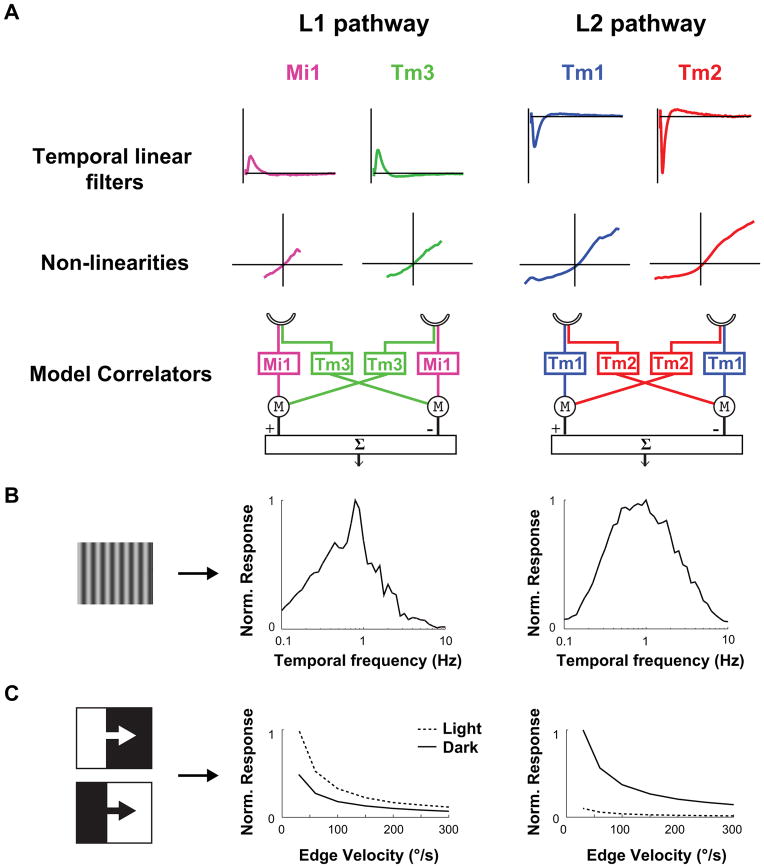
Figure 4. Modeling Mi1/Tm3 and Tm1/Tm2 as the delayed and non-delayed channels of light edges and dark edges correlators.
A. Left: The average filters and nonlinearities from the receptive field stochastic data set (200 s noise presentation, 50 ms correlation time, Extended data Figure 6) were used to model Mi1 and Tm3 as the delayed and non-delayed channels of a correlator model in bottom left. Right: same as left with Tm1 and Tm2 as the delayed and non-delayed channels of correlator model.
B. Computed normalized temporal frequency tuning curves obtained numerically for the Mi1/Tm3 model correlator (left) and the Tm1/Tm2 model correlator (right) using sine waves of different temporal frequencies.
C. Computed normalized response of the Mi1/Tm3 model correlator (left) and Tm1/Tm2 model correlator (right) to light or dark edges of 100% contrast, moving at a range of speeds.