Figure 3.
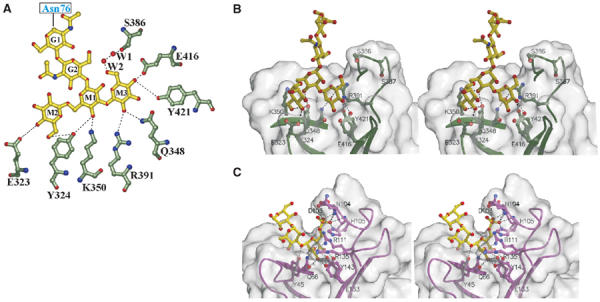
Man3GlcNAc2-binding site. (A) Flattened view of the ligand-binding site. Oligosaccharide residues are shown with the single letter code G for GlcNAc and M for mannose. M3 is joined to M1 via an α1–3 linkage, whereas M2 is joined to M1 via an α1–6 linkage. The two water molecules (W1 and W2) are bridging between the 6-hydroxyl of M3 and Ser386. Gln348, Arg391, Glu416, and Tyr421 correspond to conserved residues found in the Man-6-P-binding pocket of the CD-MPR crystal structure (Roberts et al, 1998; Olson et al, 1999), and previous mutagenesis studies demonstrate the essential nature of these residues for Man-6-P binding by a construct encoding domains 1–3 of the CI-MPR (Dahms et al, 1993; Hancock et al, 2002a). (B) Stereo diagram of the ligand-binding pocket of domains 1–3 showing the molecular surface of the protein. Potential hydrogen bonds between side chains and ligand are shown by the dotted lines. (C) Stereo diagram of the ligand-binding pocket of the CD-MPR in complex with pentamannosyl phosphate (PDB code, 1C39), showing the molecular surface of the protein. Potential hydrogen bonds between side chains and ligand are shown by the dotted lines.
