Figure 1.
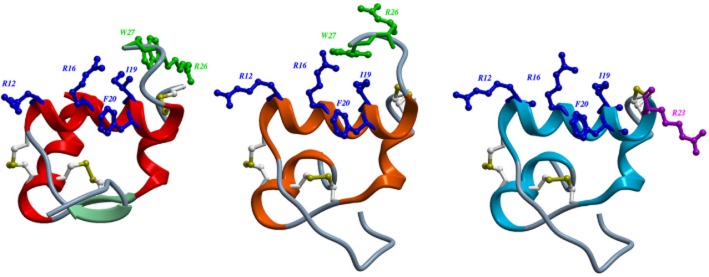
Structures of H3 relaxin (A); chimeric H3 relaxin B-chain/INSL5 A-chain (R3/I5) (B) and R3(BΔ23–27)R/I5 (C). The structures of H3 relaxin (2fhw) and R3/I5) (2k1v) were downloaded from the RSCB protein data bank and displayed using ICM-pro (Molsoft L.L.C., San Diego, CA, USA). The heterodimeric peptides contain an A-chain and B-chain linked by disulphide bonds (Bathgate et al., 2002; 2006a). Residues important for RXFP3 binding are in blue and for activation in green. Arg23 in R3(BΔ23–27)R/I5 is important for antagonist activity and shown in purple (Kuei et al., 2007; Hossain et al., 2009). (A) The NMR structure of H3 relaxin (Rosengren et al., 2006). (B) R3/I5 comprises the H3 relaxin B-chain and the human INSL5 A-chain (Sutton et al., 2004). NMR studies indicate that R3/I5 has a very similar structure to H3 relaxin (Haugaard-Jonsson et al., 2008). (C) The R3/I5 analogue, R3(BΔ23–27)R/I5 has the C-terminus of the B-chain truncated and with a terminal Arg residue (Kuei et al., 2007; Hossain et al., 2009).
