Abstract
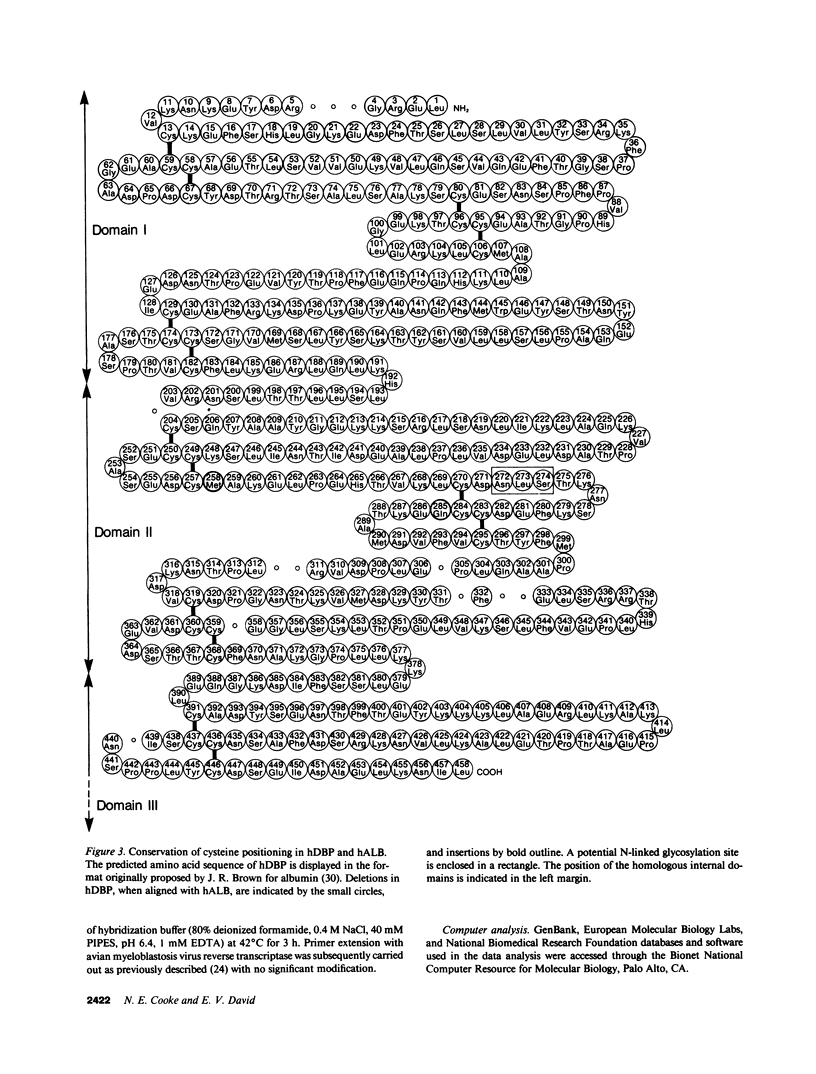
A near full-length cDNA encoding the human vitamin D-binding protein (hDBP) was isolated from a human liver mRNA expression library. Complete sequence analysis of this clone predicts the full-length amino acid sequence of the pre-hDBP. Comparison of the sequence of the hDBP mRNA and protein to existing protein and nucleic acid data banks demonstrates a strong and highly characteristic homology of the hDBP with human albumin (hALB) and human alpha-fetoprotein (hAFP). Based upon this structural comparison, we establish that DBP is a member of the ALB and AFP gene family.
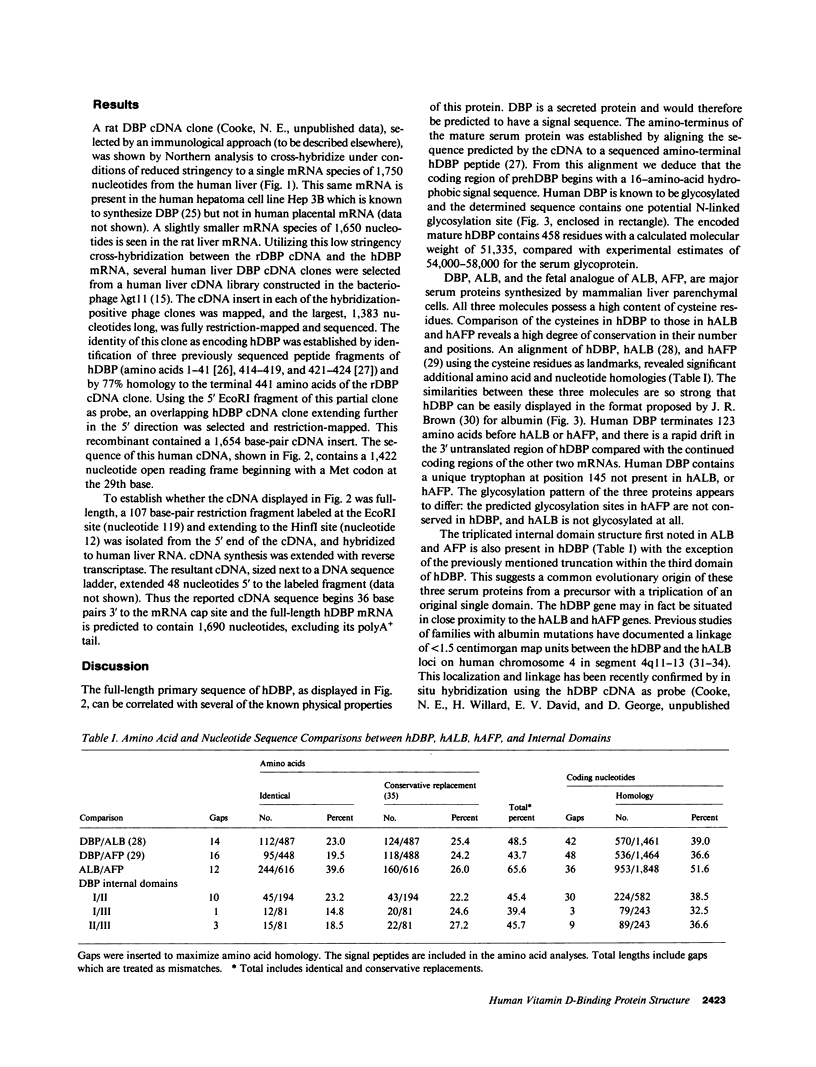
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R. Structural origins of mammalian albumin. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2141–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Coit D., Weiner R. I., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Structure of cloned DNA complementary to rat prolactin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6502–6510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
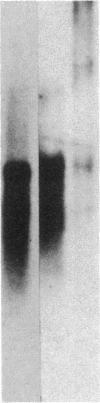
- Cooke N. E., Walgate J., Haddad J. G., Jr Human serum binding protein for vitamin D and its metabolites. II. Specific, high affinity association with a protein in nucleated tissue. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5965–5971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Schanfield M. S., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Group-specific component (Gc) proteins bind vitamin D and 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2076–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Law S. W., Dennison O. E. Nucleotide sequence and the encoded amino acids of human serum albumin mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):71–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Aden D. P., Kowalski M. A. Characterization of the human plasma binding protein for vitamin D and its metabolites synthesized by the human hepatoma-derived cell line, Hep 3B. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6850–6854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Jr Transport of vitamin D metabolites. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979 Jul-Aug;(142):249–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Dugaiczyk A. Linkage of the evolutionarily-related serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes within q11-22 of human chromosome 4. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Jul;35(4):565–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaarsalo E., Melartin L., Blumberg B. S. Autosomal linkage between the albumin and Gc loci in humans. Science. 1967 Oct 6;158(3797):123–125. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3797.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length complementary DNA clone and amino acid sequence of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):556–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Kan Y. W. Differentiation of the mRNA transcripts originating from the alpha 1- and alpha 2-globin loci in normals and alpha-thalassemics. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):439–446. doi: 10.1172/JCI110273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen M., Jacobsen P., Henningsen K. Possible localization of Gc-System on chromosome 4. Loss of long arm 4 material associated with father-child incompatibility within the Gc-System. Hum Hered. 1977;27(2):105–107. doi: 10.1159/000152857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinaga T., Sakai M., Wegmann T. G., Tamaoki T. Primary structures of human alpha-fetoprotein and its mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4604–4608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini M., Emerson D. L., Galbraith R. M. Linkage between surface immunoglobulin and cytoskeleton of B lymphocytes may involve Gc protein. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):73–74. doi: 10.1038/306073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini M., Galbraith R. M., Emerson D. L., Nel A. E., Arnaud P. Structural studies of T lymphocyte Fc receptors. Association of Gc protein with IgG binding to Fc gamma. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1804–1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoentgen F., Metz-Boutigue M. H., Jollès J., Constans J., Jollès P. Homology between the human vitamin D-binding protein (group specific component), alpha-fetoprotein and serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80738-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svasti J., Kurosky A., Bennett A., Bowman B. H. Molecular basis for the three major forms of human serum vitamin D binding protein (group-specific component). Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1611–1617. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Baelen H., Bouillon R., De Moor P. Vitamin D-binding protein (Gc-globulin) binds actin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2270–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitkamp L. R., Rucknagel D. L., Gershowitz H. Genetic linkage between structural loci for albumin and group specific component (Gc). Am J Hum Genet. 1966 Nov;18(6):559–571. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]