Figure 4.
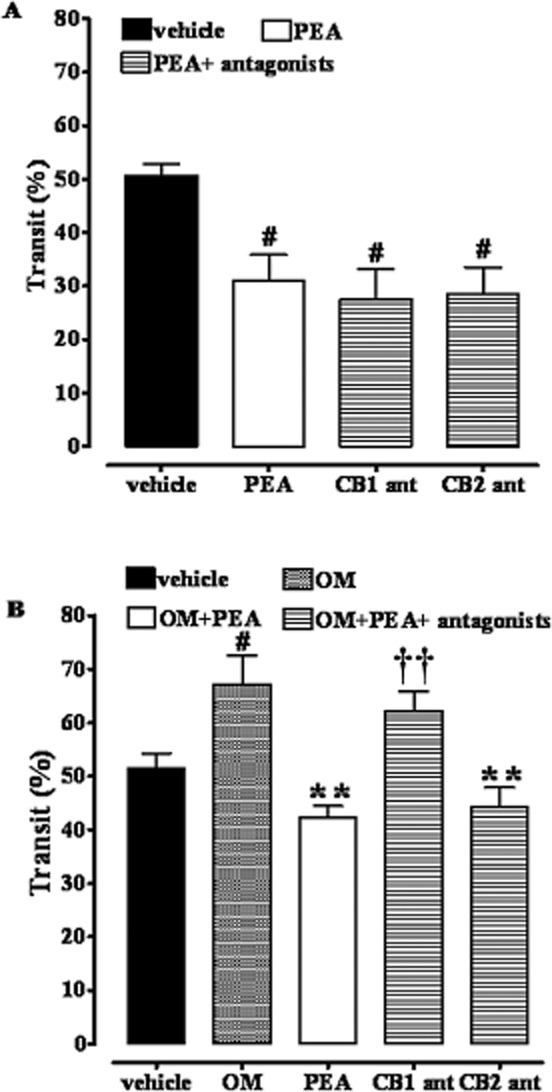
Inhibitory effect of PEA (10 mg·kg−1, i.p.) on upper gastrointestinal transit in control mice (A) and in OM-treated mice (B) in the presence of rimonabant (CB1 ant, 0.1 mg·kg−1, i.p.) or SR144528 (CB2 ant, 1 mg·kg−1, i.p.). Transit was measured 28 days after OM or vehicle (30% ethanol) administration. Results (the means ± SEM of six to eight mice for each experimental group) are expressed as a percentage of upper gastrointestinal transit. #P < 0.05, significantly different from vehicle; **P < 0.01, significantly different from OM; ††P < 0.01, significantly different from PEA. Note that in (A) the term ‘vehicle’ refers to the vehicle used to dissolve PEA, while in (B) the term ‘vehicle’ refers to the vehicle used to dissolve OM.
