Figure 5.
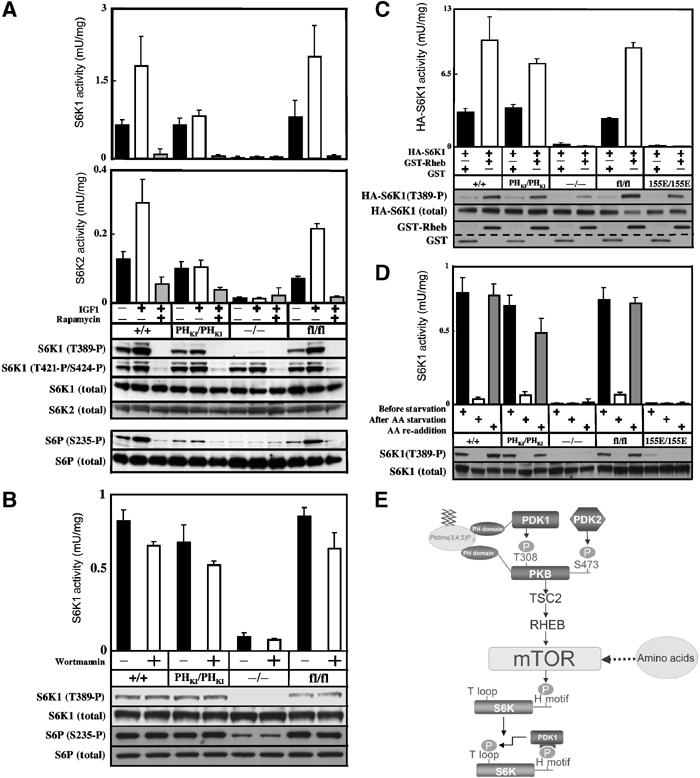
Regulation of S6K in PDK1(PHKI/PHKI) cells. (A) The indicated ES cell lines were grown to 80% confluence and serum starved for 3.5 h, incubated with or without 100 nM rapamycin for 30 min and then either left unstimulated or stimulated with 20 ng/ml IGF1 for 15 min. The cells were lysed and the activity of S6K1 (upper panel) or S6K2 (lower panel) was measured in independent experiments after immunoprecipitation using antibodies specific for either isoform. The results shown are mean±s.d. for three dishes of cells each assayed in duplicate. The activation of S6K and phosphorylation of its substrates were assessed using the indicated phosphospecific antibodies. (B) As above, except that serum-deprived cells were incubated in the presence or absence of 100 nM wortmannin for 10 min. (C) ES cells were transfected with HA epitope-tagged S6K1 (HA-S6K1) in the presence of either GST-Rheb or GST alone. At 24 h post-transfection, cells were serum starved for 4 h and HA-S6K1 immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody. The immunoprecipitates were either assayed for S6K1 activity or immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The levels of GST-Rheb and GST were determined by immunoblotting cell lysates with anti-GST. The dotted line emphasizes the molecular weight difference between GST-Rheb and GST. (D) ES cell lines were grown to 80% confluence and deprived of serum but not amino acids for 2.5 h. The cells were then either maintained in the presence of amino acids for 90 min (before starvation) or deprived of amino acids for 90 min (AA starvation) or deprived of amino acids for 90 min followed by the re-addition of amino acids for 30 min (AA re-addition). S6K activity and phosphorylation were assessed as above. Similar results were obtained in at least two separate experiments. (E) Model summarising the mechanism of activation of S6K by the PI 3-kinase and amino acids that is discussed in the main text.
