Figure 2.
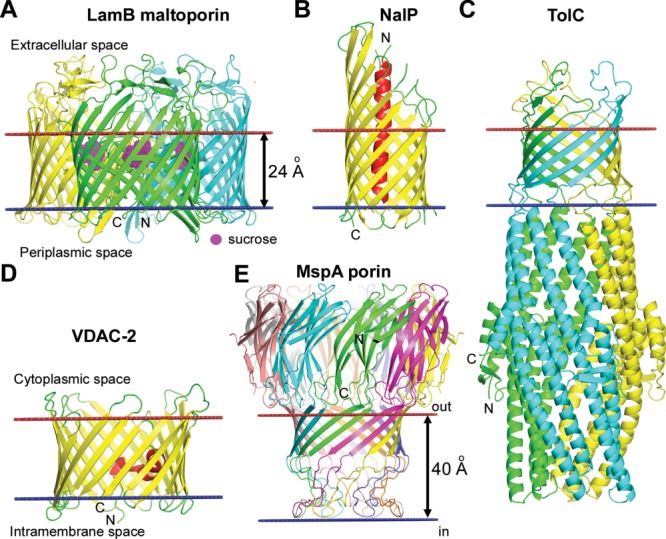
Different types of TM β-barrels. (A) Trimer of maltoporin LamB from the OM of E. coli with sucrose in the hydrophilic channel (1AF6). Each monomer of the sugar transporter represents a 18-stranded single-chain TM β-barrel with a channel that selects sugars through interaction with aromatic residues. (B) Monomer of NalP autotransporter from the OM of Neisseria meningitides (1UYO). NalP is a 12-stranded single-chain TM β-barrel with the N-terminal passenger domain (red helix) inside the pore that can be released after the self-cleavage. (C) Multichain β-barrel of TolC from the OM of E. coli (1EK9). 12-Stranded β-barrel of TolC is formed by homotrimer. (D) Single chain β-barrel of mitochondrial voltage dependent anion channel VDAC-2 from the MOM of Danio rerio (4BUM). VDAC-2 represents a 19-stranded TM β-barrel with N-terminal amphiphilic α-helix located inside the circular channel, which is involved in voltage sensing. (E) Multichain β-barrel of MspA porin from the OM of Mycobacterium smegmatis (1UUN). The stem domain of MspA represents a 16-stranded β-barrel formed by homo-octamer. Calculated membrane boundaries from the OPM database are shown by red and blue lines.
