Figure 4.
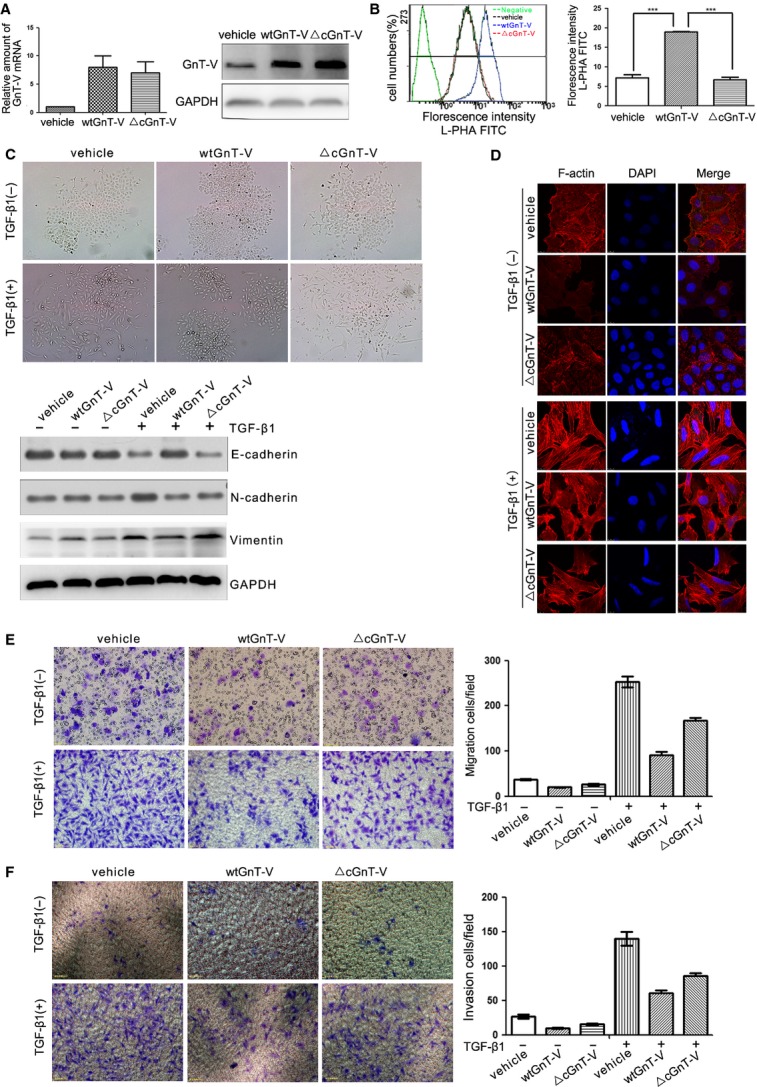
Overexpression of GnT-V in A549 cells suppresses TGF-β1-induced EMT, cell migration and invasion in a catalytic activity–dependent manner. (A) GnT-V overexpression stable A549 cells were established by using lentiviral gene specific for wild-type GnT-V (wtGnT-V) or inactive mutant GnT-V (△cGnT-V) system and selected by using puromycin. The GnT-V mRNA (left) and protein (right) levels in stable cells were determined by qRT-PCR and western blot respectively. (B) The cell surface β1,6-GlcNAc branched N-glycans of GnT-V overexpression stable A549 cells were quantified by flow cytometry with L-PHA lectin, the negative control showing the background fluorescence. A representative result of three independent experiments (left) and statistic data (right) were presented. (C and D) Overexpression of GnT-V in A549 cells suppresses TGF-β1 (5 ng/ml; 48 hrs)-induced EMT in a catalytic activity–dependent manner, as determined by the cell morphological changes (C, top), the expression levels of EMT markers (E-cadherin and N-cadherin) by western blot (C, bottom) and the actin remodelling by immunofluorescence staining the F-actin (D). (E) Overexpression of GnT-V in A549 cells suppresses TGF-β1 (5 ng/ml; 48 hrs)-induced cell migration in a catalytic activity–dependent manner, as determined by transwell assay. A representative result of three independent (left) and statistic data (right) were presented. (F) Overexpression of GnT-V in A549 cells suppresses TGF-β1 (5 ng/ml; 48 hrs)-induced cell invasion in a catalytic activity–dependent manner, as determined by transwell assay with matrigel. A representative result of three independent experiments (left) and statistic data (right) were presented.
