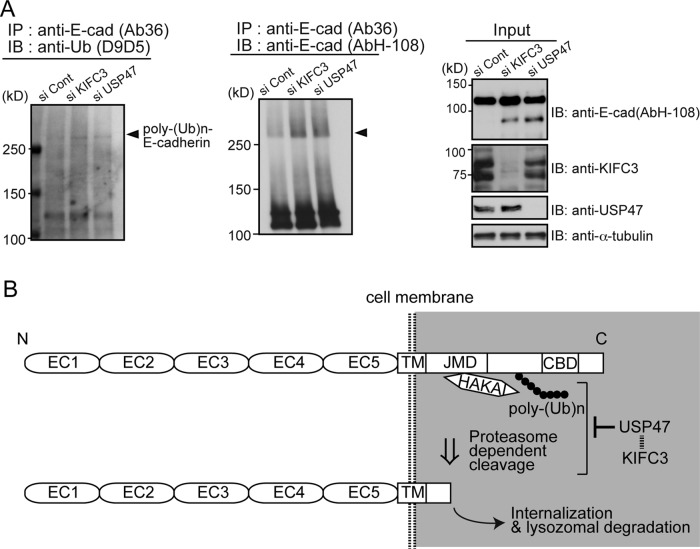
FIGURE 5:
KIFC3 and USP47 are required to suppress E-cadherin ubiquitination. (A) Western blotting detection of ubiquitin from E-cadherin using D9D5, an antibody that detects only the polyubiquitin chains formed by Lys-48 residue linkage (left), and that of putative ubiquitinated E-cadherin (middle). Left, cells were harvested at 48 h after transfection with siRNAs. From their lysates, E-cadherin was immunoprecipitated using Ab36, and the precipitates were analyzed to detect polyubiquitinated bands. Middle, E-cadherin was immunoprecipitated using Ab36, and the precipitates were analyzed with AbH-108. Smeared E-cadherin bands with high molecular sizes increase after KIFC3 or USP47 depletion. Arrowheads indicate the position of D9D5-positive bands. Right, input samples. (B) Working model for the role of KIFC3 and USP47 in E-cadherin homeostasis. E-cadherin is polyubiquitinated by Hakai and cleaved at an intracellular site by proteasomes. USP47 inhibits these processes to maintain E-cadherin at cell–cell contacts. The ubiquitinated site is drawn hypothetically.