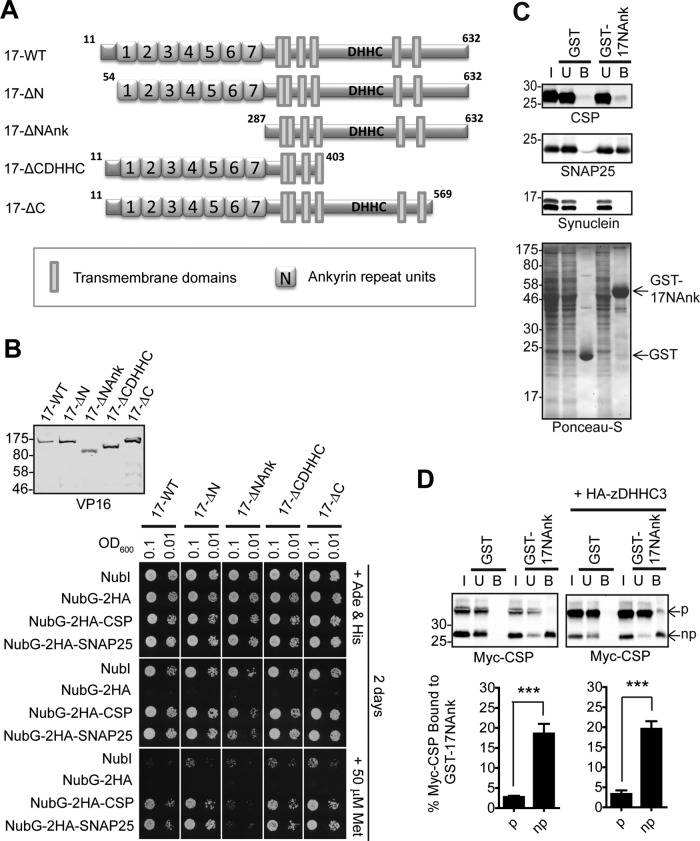
FIGURE 3:
The ANK domain of zDHHC17 is both necessary and sufficient for binding to CSP and SNAP25. (A) Schematic diagram of zDHHC17 truncation mutants used for SUS analysis. (B) Detection of CSP and SNAP25 interactions with zDHHC17 wild type (17-WT) and 17-ΔN, 17-ΔNAnk, 17-ΔCDHHC, and 17-ΔC truncation mutants using SUS (growth assay). zDHHC17– CSP/SNAP25 matings at corresponding OD600 were dropped on SD medium supplemented with adenine and histidine to verify equal dropping densities, and on SD medium (supplemented or not with methionine) to verify interactions. Plates were scanned after incubation at 30°C for 2 d. Spontaneous reassembly of the C-terminal ubiquitin of zDHHC17-Cub-PLV with wild-type (NubI) or mutated (NubG) N-terminal ubiquitin was assessed in parallel. Top left, Western blot detection of zDHHC17-Cub-PLV truncation mutants (anti-VP16 antibody) and NubG-2HA-CSP/SNAP25 (anti-HA antibody) from haploid-yeast lysates, along with positions of molecular weight markers. (C) Interaction of GST-tagged, N-terminal cytosolic domain (amino acids11–305) of zDHHC17 (GST-17NAnk) with SNAP25 and CSP from rat brain. GST-precleared rat brain lysate was incubated with glutathione beads and either GST or GST-17NAnk; bound proteins were eluted after boiling in sample buffer and centrifugation. Input (I; 0.2%), unbound (U; 0.2%), and bound fractions (B; 1%) were subjected to SDS–PAGE, transfer to nitrocellulose, Ponceau-S staining, and Western blot analysis using the antibodies indicated. Positions of molecular weight markers are shown on the left. (D) Top, interaction of GST-17NAnk with palmitoylated (p) and nonpalmitoylated (np) Myc-tagged CSP. HEK293T cells were either transfected with Myc-CSP alone or cotransfected with Myc-CSP and HA-zDHHC3 plasmids; precleared HEK293T lysate was incubated with glutathione beads and purified GST or GST-17NAnk; bound proteins were eluted after boiling in sample buffer and centrifugation. Input (I; 6%), unbound (U; 5%), and bound fractions (B; 20%) were subjected to SDS–PAGE, transfer to nitrocellulose, Ponceau-S staining, and Western blot analysis using anti-Myc antibody. Positions of molecular weight markers are shown on the left. Bottom, percentage of Myc-CSP recovered was quantified for both p and np (n = 4; error bars, SEM), and differences were statistically analyzed by unpaired Student's t test (***p < 0.001).