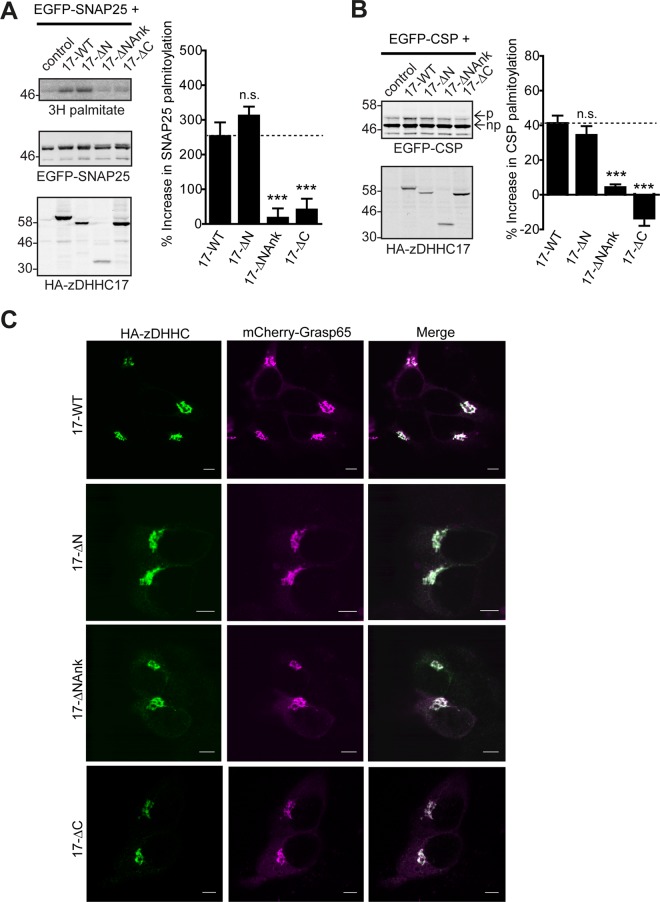
FIGURE 4:
The ANK domain and cytosolic C-terminal domain of zDHHC17 are required for S-acylation of SNAP25 and CSP. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with EGFP-SNAP25 (A) or EGFP-CSP (B), and an appropriate amount of the indicated HA-tagged zDHHC17 constructs (per well) or control (empty HA-pEF-BOS vector) to achieve similar zDHHC17 expression levels (17-WT and 17-ΔN, 2.4 μg;17-ΔNAnk and control, 3.2 μg; 17-ΔC, 1.6 μg). EGFP-SNAP25 and HA-zDHHC enzymes were detected by immunoblotting with GFP and HA antibodies, respectively, and incorporation of radiolabel was detected with the aid of a Kodak Biomax Transcreen LE. Positions of molecular weight markers are shown on the left. SNAP25 palmitoylation was assessed by the amount of 3H-palmitic acid incorporated (after metabolic labeling) relative to protein levels, and CSP palmitoylation was assessed, after separation of its palmitoylated (p) and nonpalmitoylated (np) forms by SDS–PAGE of cell lysates and immunoblotting with GFP, by calculating the ratio of palmitoylated EGFP-CSP (p) to the total protein (p + np). Percentage increase in palmitoylation (vs. control) was quantified (n = 4; error bars, SEM) and differences from 17-WT were analyzed by Tukey posttest, following a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA; n.s., p ≥ 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Subcellular distribution of zDHHC17 constructs was assessed by cotransfection with Golgi marker GRASP65 (mCherry construct) and immunofluorescence using an HA antibody (C). Scale bars, 5 μm.