FIGURE 6:
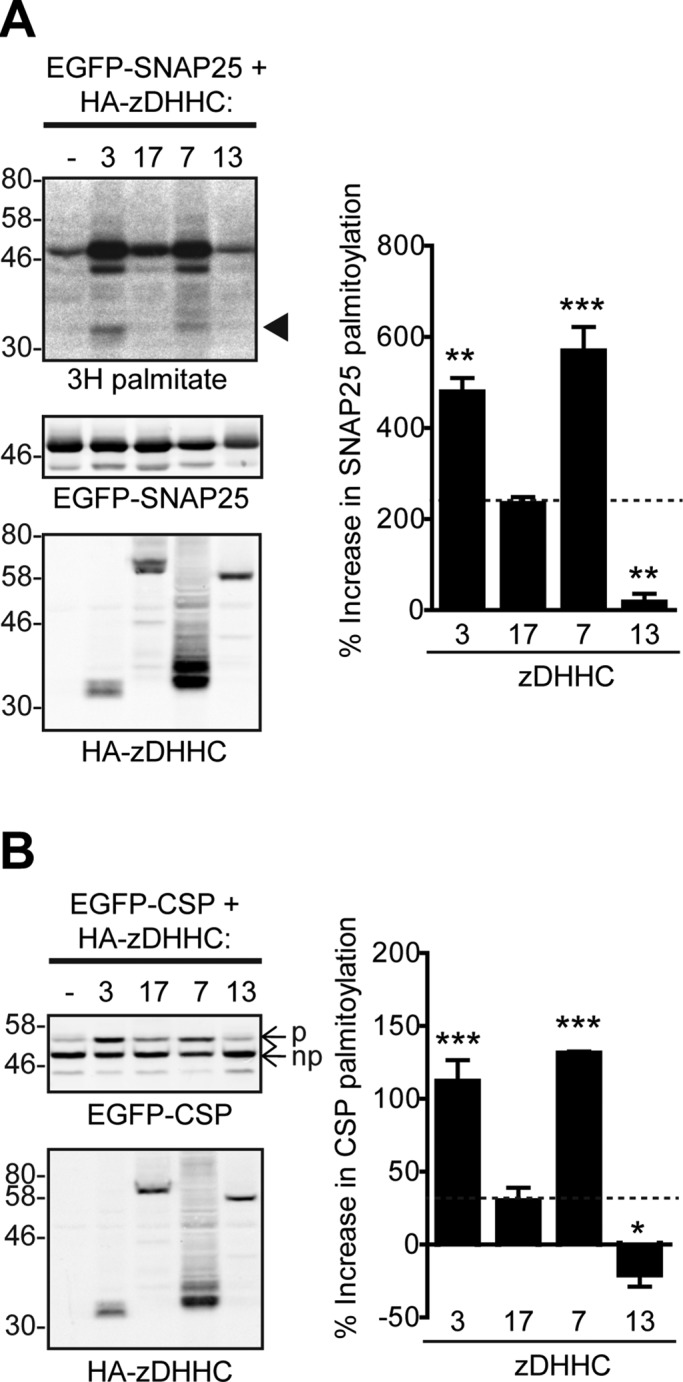
zDHHC3 and zDHHC7 can S-acylate CSP and SNAP25 more efficiently than zDHHC17, whereas zDHHC13 is inactive toward these substrates. (A) S-acylation of SNAP25 by zDHHC3, 17, 7, and 13. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with EGFP-SNAP25 and the indicated HA-tagged zDHHCs (or empty vector as control) and labeled with 3H-palmitate as described in Materials and Methods. EGFP-SNAP25 and HA-zDHHC enzymes were detected by immunoblotting with GFP and HA antibodies, respectively, and incorporation of radiolabel was detected with the aid of a Kodak Biomax Transcreen LE. Positions of molecular weight markers are shown on the left. Arrowhead indicates autoacylated zDHHC3/zDHHC7. SNAP25 palmitoylation was assessed by the amount of 3H-palmitic acid incorporated relative to protein level. Percentage increase in palmitoylation (vs. control) was quantified (n = 4; error bars, SEM), and differences from zDHHC17-induced palmitoylation were analyzed by Tukey posttest, following a one-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). (B) S-acylation of CSP by zDHHC3, 17, 7, and 13. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with EGFP-CSP and the indicated HA-tagged zDHHC. EGFP-CSP and HA-zDHHC enzymes were detected by immunoblotting with GFP and HA antibodies, respectively. CSP palmitoylation was assessed, after separation of its palmitoylated (p) and nonpalmitoylated (np) forms by SDS–PAGE of cell lysates, by calculating the ratio of palmitoylated EGFP-CSP (p) to the total protein (p + np). Percentage increase in palmitoylation (vs. control) was quantified (n = 4; error bars, SEM), and differences from zDHHC17-induced palmitoylation were analyzed by Tukey posttest, following a one-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
