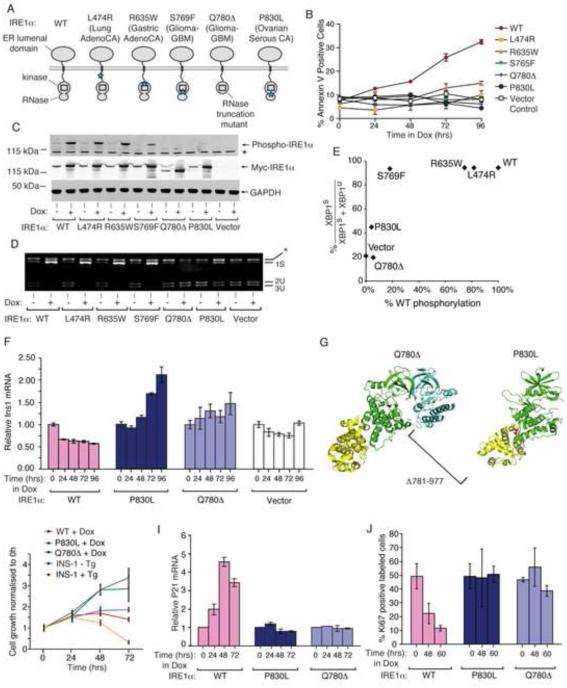
Figure 2. IRE1α cancer mutants are disabled for apoptosis.
(A) Cancer-associated mutations in human IRE1α. (B) Time course Annexin-V staining of INS-1 cells stably expressing human IRE1α (WT), (L474R), (R635W), (S765F), (Q780*), and (P830L) under saturating Dox (1μg/ml). (C) Anti-phospho-IRE1α and anti-Myc immunoblots, and (D) agarose gel of PstI-digested XBP1 cDNA amplicons from INS-1 cells expressing human IRE1α (WT) and mutants with Dox (1μg/ml) for 24hr. (E) XBP1 splicing from (D) as a function of IRE1α phosphorylation from (C). (F) Time course Q-PCR of Ins1 mRNA from INS-1 cells expressing IRE1α (WT) and mutants under Dox (1μg/ml). (G) Cartoon of monomeric human IRE1α (P830L) (right panel) and IRE1α (Q780*) dimerized with a IRE1α (WT) subunit (left panel) based on PDB: 3P23. (H) Time course MTT staining of INS-1 cells expressing IRE1α (WT), IRE1α (P830L) or IRE1α (Q780*) −/+ Dox (1μg/ml), or parental INS-1 cells −/+ 100 nM Tg. (I,J) Time-course Q-PCR for p21 mRNA, and Ki67 staining, from INS-1 IRE1α (WT), IRE1α (P830L) or IRE1α (Q780*) cells under Dox (1μg/ml). Three independent biological samples were used for Q-PCR, Ki67, and Annexin V experiments. Data plotted as mean +/− SD. Also see Figure S2.