Figure 2.
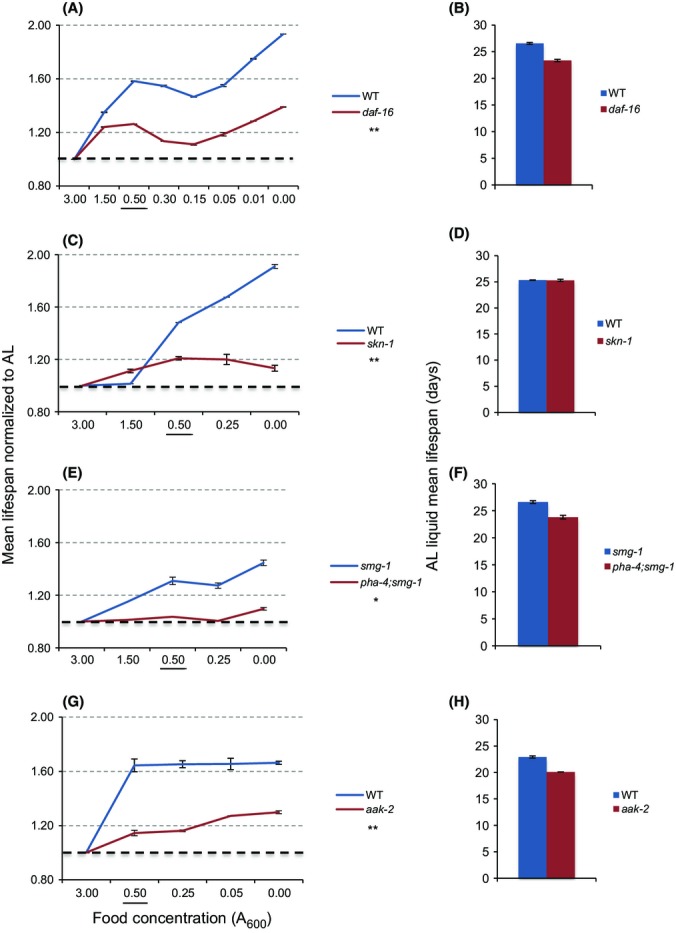
Importance of stress response mechanisms for DR lifespan extension. (A) Lack of DAF-16 impaired DR lifespan extension. AL lifespans obtained in parallel are shown in (B). (C,D) skn-1 was required for DR to extend lifespan. Whereas WT worms experienced an average of 48.3% and 91.0% increase in lifespan upon DR and DD, respectively, these increases were only 20.9% and 13.3% in predicted null skn-1 mutants. (D) Under AL liquid conditions, skn-1 mutants’ mean lifespan was equal to that of WT, in contrast to results obtained on plates (Tullet et al., 2008). (E, F) pha-4(zu225) mutation eliminated DR longevity in the control smg-1(cc546ts) background. smg-1 lifespan was increased 33.2% by DR and 38.8% by DD, respectively. (G,H) The AMPK subunit AAK-2 is required for full DR and DD lifespan extension. Composites of all analyses are shown, with individual experiments presented in Table S13 (Fig.2A,B), Table S14 (Fig.2C,D), Table S15 (Fig.2E,F), and Table S16 (Fig.2G,H). Two-way ANOVA analysis across the bacterial gradient (compared to control): *P = 0.0004, **P = 0.0001. The food concentration 0.50 A600 is underlined to facilitate comparison of results.
