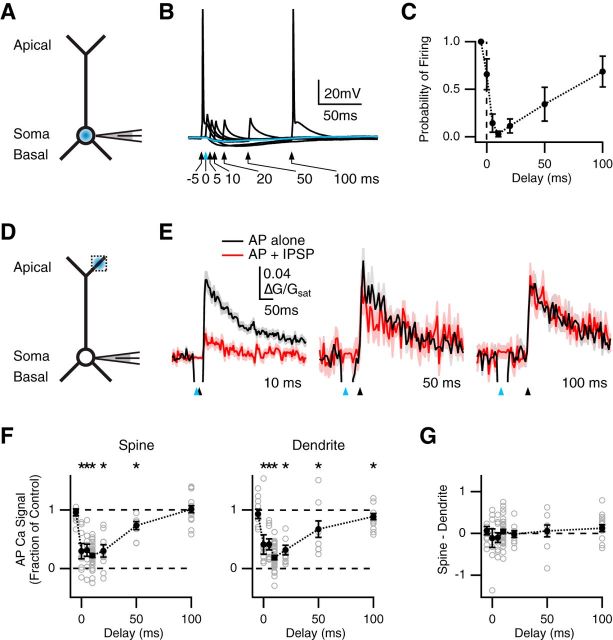
Figure 3.
Temporally precise inhibition of spines and dendrites. A, Schematic of recording configuration, where the blue spot indicates GABA uncaging at the soma. B, Influence of somatic GABA uncaging on AP firing, where the blue arrow and trace indicate uncaging pulse at t = 0 ms, and black arrows and traces indicate AP paired with uncaging at different delays. C, Summary of firing probability versus delay between AP and uncaging pulse. D, Similar to A with GABA uncaging at the apical dendrite, where the dotted box indicates location of imaged spines and dendrites. E, Average Ca2+ signals evoked in apical spines by AP alone (black) or AP paired with GABA uncaging (red), with 10 ms (left), 50 ms (middle), or 100 ms (right) delay, where blue arrows indicate uncaging pulse and black arrows indicate AP firing. F, Summary of impact of GABA uncaging on AP Ca2+ signals in spines (left) or dendrites (right) versus delay between AP and uncaging pulse. *p < 0.05. G, Summary of difference in inhibition at spines and dendrites, where values above zero indicate less inhibition at spines, and values below zero indicate more inhibition at spines, showing no difference at any delay.