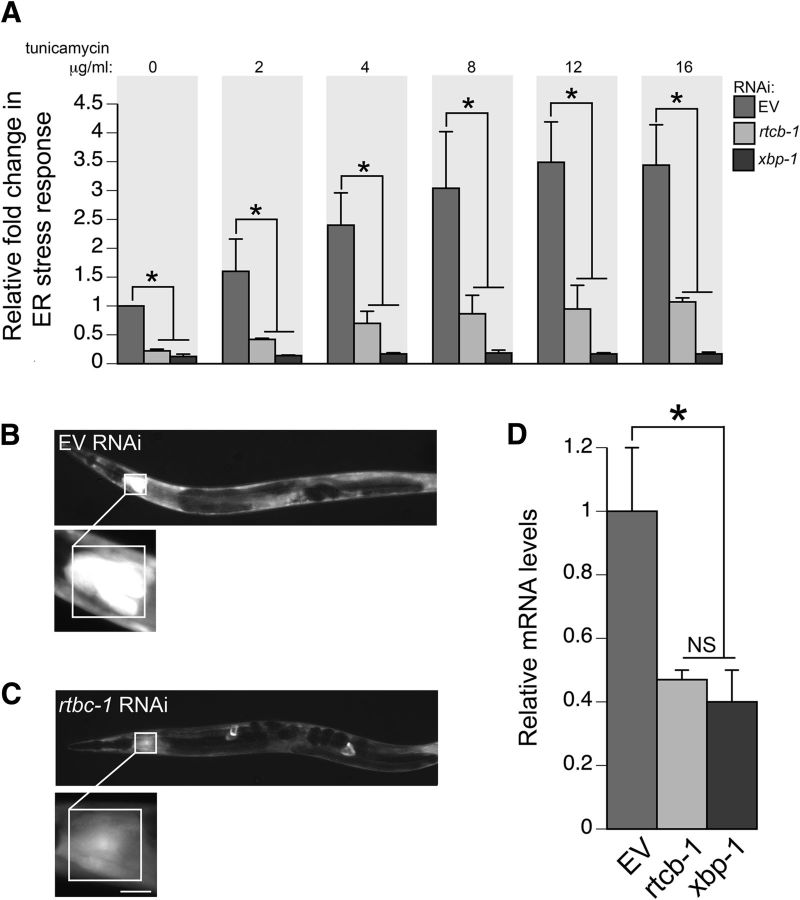
Figure 3.
Knockdown of RTCB-1 lowers ER stress response. A, Bar charts of GFP intensity from the stress reporter hsp-4::GFP alone (with EV RNAi) or after RNAi knockdown of rtcb-1 or xbp-1 measured consistently in the regions shown in B and C. Strains were treated with increasing concentrations of tunicamycin for 6 h (or DMSO as control). Data presented have been normalized to EV RNAi, untreated, hsp-4::GFP samples and is calculated as the mean ± SD of three experiments, in which 30 animals were analyzed per replicate (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). RNAi knockdown of both rtcb-1 and xbp-1 (positive control) caused significant downregulation of hsp-4::GFP expression. B, C, Representative C. elegans images for RNAi treatments described in A. Pixel intensities were measured in a 100 × 100 μm region of the intestine proximal to the pharynx. The region highlighted in the white box shows GFP expression driven by the hsp-4 gene promoter that was measured in all animals. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, RNAi depletion of rtcb-1 and xbp-1 (positive control) in N2 worms caused a decrease in hsp-4 mRNA expression when compared with EV control, as shown by qPCR (*p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). Values are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments and were normalized to the control.