Figure 1.
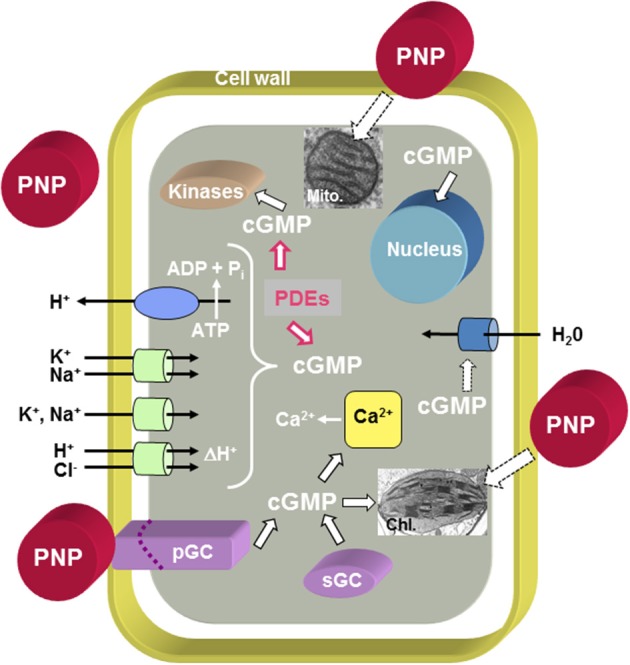
Overview of PNP action at the cellular level. The model proposes that PNPs can dock to receptor-like molecules with ligand-inducible guanylate cyclase activity (pGCs) and that cGMP acts as second messenger while phosphodiesterases (PDEs) metabolize cGMP to GMP. Cyclic GMP can affect cytosolic Ca2+ levels by modulating ion channels [e.g., Cyclic Nucleotide Gated Channels (CNGCs)], activate phosphorylation through kinases and in turn affect the transcriptome and (phospho-)proteome. It is also conceivable that PNP acts directly or indirectly via PNP-dependent phosphorylation on aquaporins. There is also evidence for PNP-dependent modulation of chloroplast and mitochondrial function. Solid black outlined arrows indicate established functions, red outlined arrows indicate inhibitory effects, and dashed outlined arrows indicate that the effects require further elucidation.
