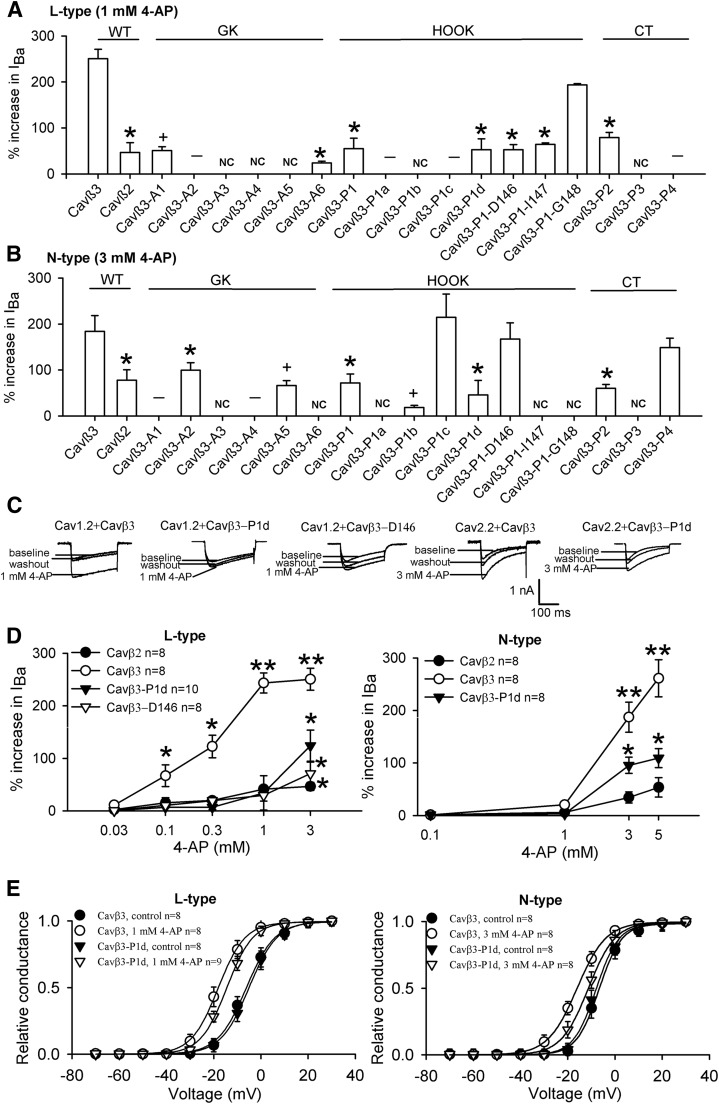
Fig. 7.
Residues in the GK, HOOK, and C-terminus domains critically determine the potentiating effect of 4-AP on N-type and L-type Ca2+ channels. (A and B) Summary data show the distinct effects of 4-AP on L-type [Cav1.2, (A)] and N-type [Cav2.2, (B)] currents in HEK293 cells reconstituted with α2δ1 and various Cavβ3 mutants (n = 6–8 cells in each group). (C and D) Original current traces and group data show that the potentiating effects of 4-AP on L-type and N-type currents were reduced in cells transfected with Cavβ3-P1d or Cavβ3-P1-D146. NC denotes no Ba2+ currents; – designates no 4-AP effects; + denotes reduced basal Ba2+ currents. (E) Effects of 4-AP on the voltage-dependent activation of L-type and N-type Ca2+ channels in HEK293 cells transfected with wild-type Cavβ3 or Cavβ3-P1d mutant. The hyperpolarizing shift in the voltage-dependence of activation of L-type and N-type Ca2+ channels by 4-AP was attenuated in cells cotransfected with Cavβ3-P1d, compared with that for the wild-type Cavβ3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the baseline control or wild-type Cavβ3 control (repeated measures analysis of variance followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test).