Figure 10.
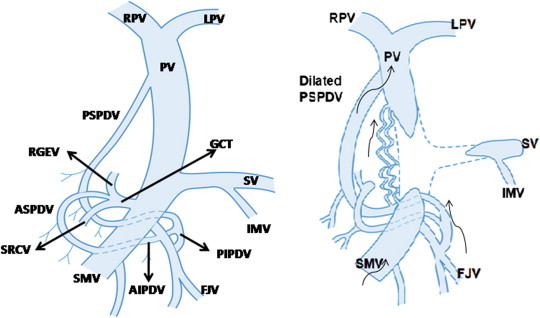
Formation of portal cavernoma: Normally the posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal vein (PSPDV) drains into portal vein (PV) close to porta hepatis and connects with posterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal vein (PIPDV) which drains into first jejunal vein (FJV), a tributary of superior mesenteric vein (SMV). The gastrocolic trunk (GCT), another tributary of SMV, is formed by union of right gastroepiploic vein (RGEV), anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal vein (ASPDV) and superior right colic vein (SRCV). In portal vein thrombosis involving the splenomesenteric confluence, the PSPDV and the pericholedochal venous plexus dilate and acts as a porto-portal collateral channels and develop into a cavernoma. Arrows indicate the direction of venous blood flow.
