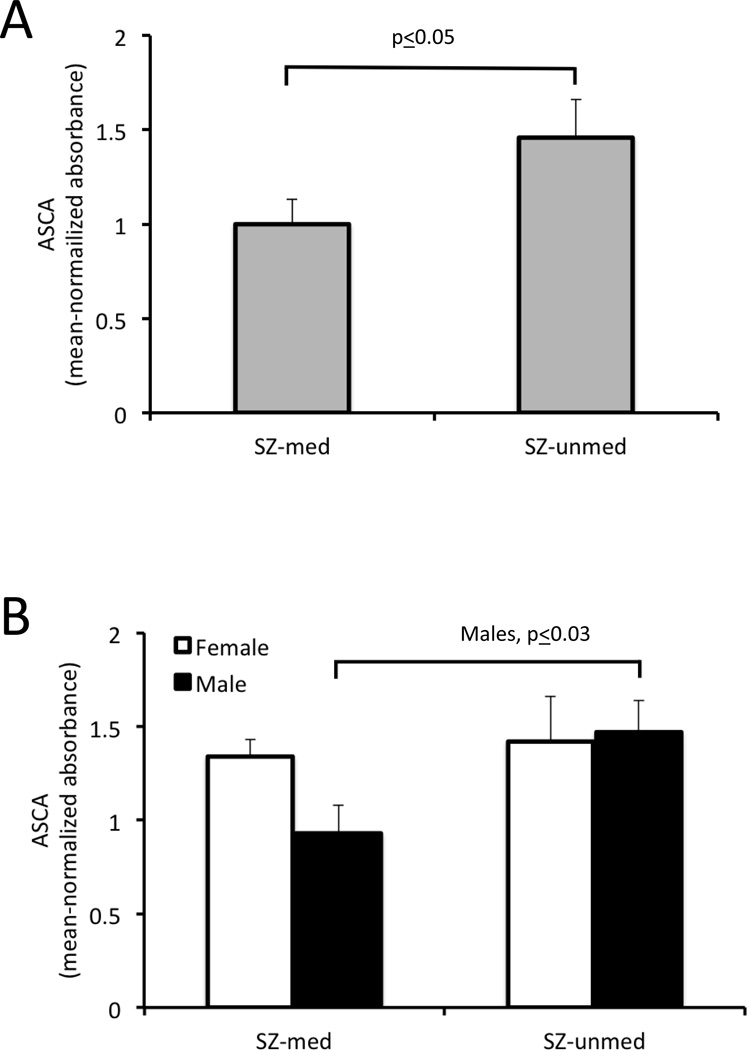
Figure 2.
ASCA IgG levels in individuals with schizophrenia according to medication status. SZ-unmed refers to antipsychotic naïve schizophrenia, and SZ-med refers to antipsychotic-positive schizophrenia. P-values refer to the level of statistical significance following a two-tailed t-test. Panel A: ASCA IgG levels were elevated in individuals who are antipsychotic naïve compared to those who received these medications. Panel B: ASCA IgG levels were significantly elevated in males who were antipsychotic naïve compared to males who were antipsychotic-positive.