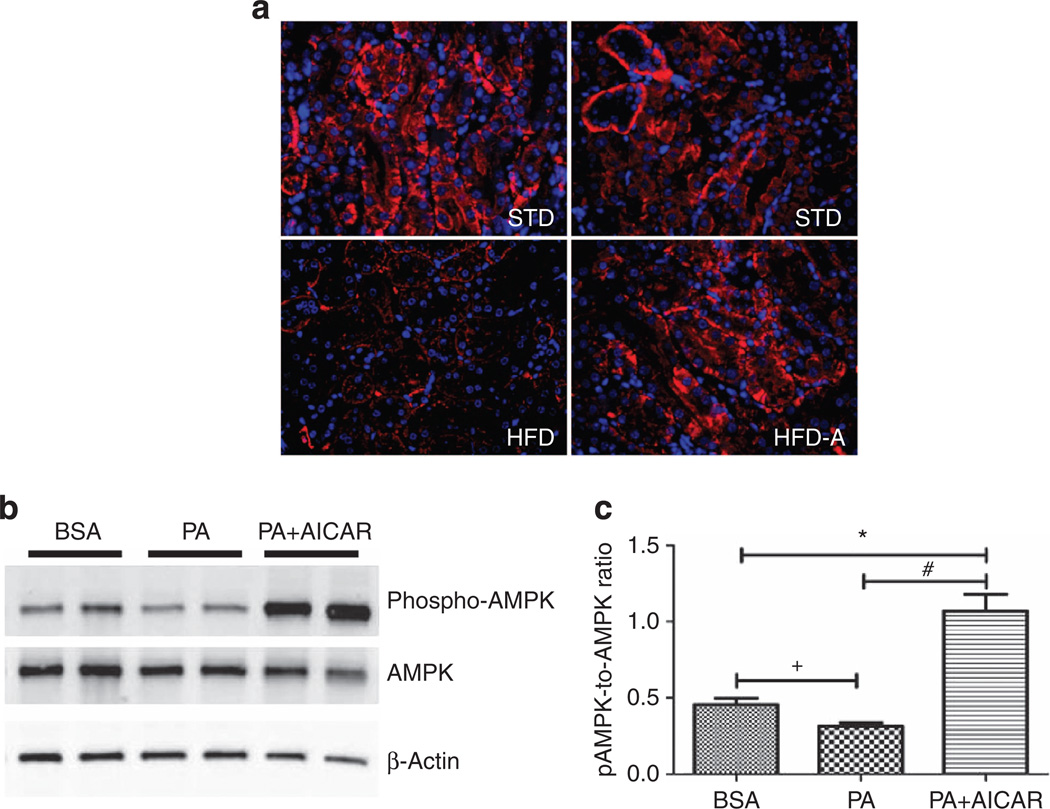
Figure 4. Effect of AICAR on AMP-activated kinase activation in renal tubular cells.
Representative immunofluorescence photomicrographs (original magnification ×400) illustrating phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) staining in kidney tissue in (a) standard diet (STD), high-fat diet (HFD), and HFD +AICAR. (b) Western blot analysis of phospho-AMPK and AMPK in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (HRPTEpiC) treated respectively with bovine serum albumin (BSA), palmitic acid (PA), or PA + AICAR in order to mimic the HFD model. (c) Relative densitometry of the immunoblot shows that phospho-AMPK was downregulated with PA in a proximal epithelial cell model, whereas the AICAR treatment significantly upregulated phospho-AMPK. Values are means ±s.e.m. N = 5 in each group. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Newman–Keuls, *P ≤ 0.05 versus BSA group and #P ≤ 0.05 versus PA group or by unpaired f-test + P ≤ 0.05 versus BSA group. AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside.