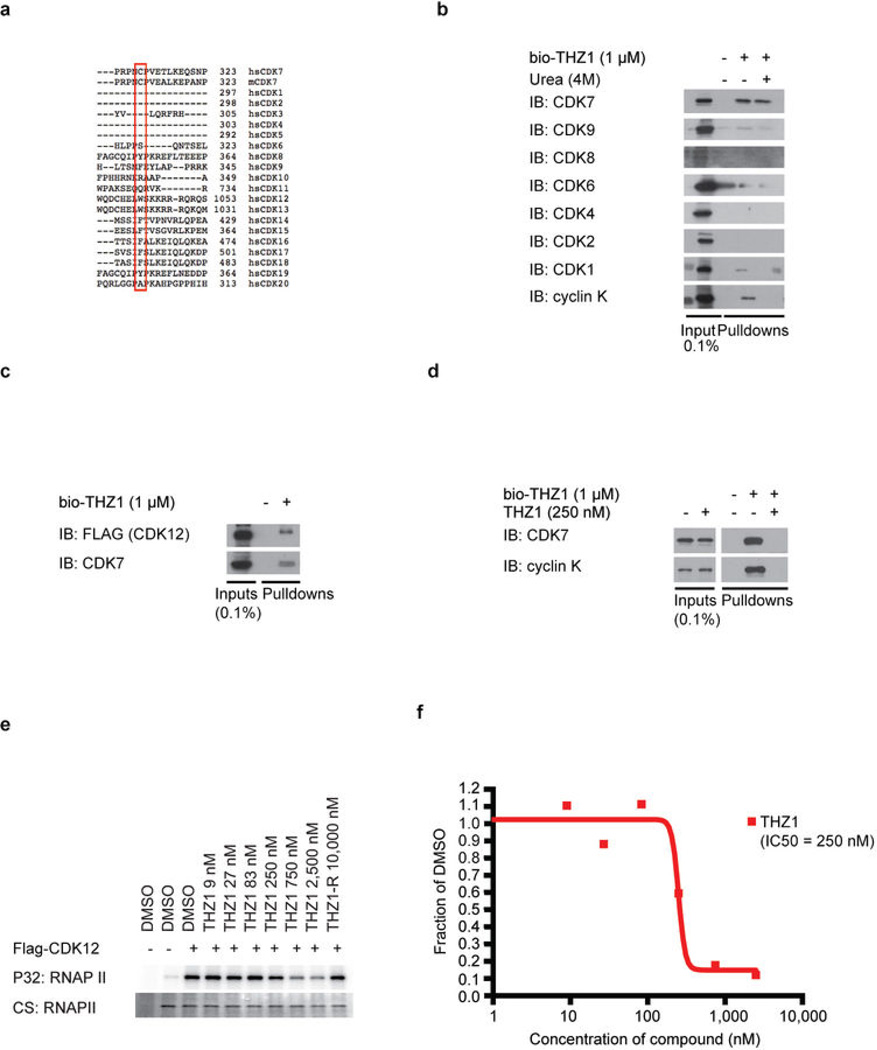
Extended Data Figure 3. THZ1 inhibits CDK12 but at higher concentrations compared to CDK7.
a, Protein sequence alignment of the C-terminal regions of all human (hs) CDKs and mouse (m) CDK7 using Uniprot default settings. Note that the canonical cell cycle CDKs 1,2,4 as well as 5 do not have C-terminal domains that extent to the equivalent position of CDK7 C312 and therefore do not display aligned sequence in this region. b, bio-THZ1 covalently pulls down CDK7 from cellular lysates. Jurkat cellular lysates were incubated with bio-THZ1 (1 µM) at 4°C for 12 hrs and 2 hrs at room temperature. Precipitated proteins were washed with or without urea (4M), here used as a denaturing agent, and probed for the indicated CDKs. c, bio-THZ1 pulls down FLAGCDK12 from lysates. Lysates from 293A cells stably expressing FLAG-tagged WT CDK12 were incubated with bio-THZ1 (1 µM) at 4°C for 12 hrs and 2 hrs at rt. Immunoprecipitated proteins were probed with FLAG antibody to recognize CDK12 or with CDK7 antibody. d, bio-THZ1 pulls down cyclin K from cellular lysates. Jurkat cellular lysates were incubated with bio-THZ1 (1 µM) at 4°C for 12 hrs and 2 hrs at rt. Precipitated proteins were probed for the indicated proteins. e, THZ1 inhibits CDK12 in an in vitro kinase assay. 293A cells stably expressing FLAG-tagged WT CDK12 were treated with THZ1 or THZ1-R for 4 hrs. Exogenous CDK12 was immunoprecipitated from cellular lysates using FLAG antibody. Precipitated proteins were washed and subjected to in vitro kinase assays at 30°C for 30 minutes using the large subunit of RNAPII (RPB1) as substrate and 25 µM ATP. CS = coomassie stain. f, Quantitation of in vitro kinase assay conducted in (d).