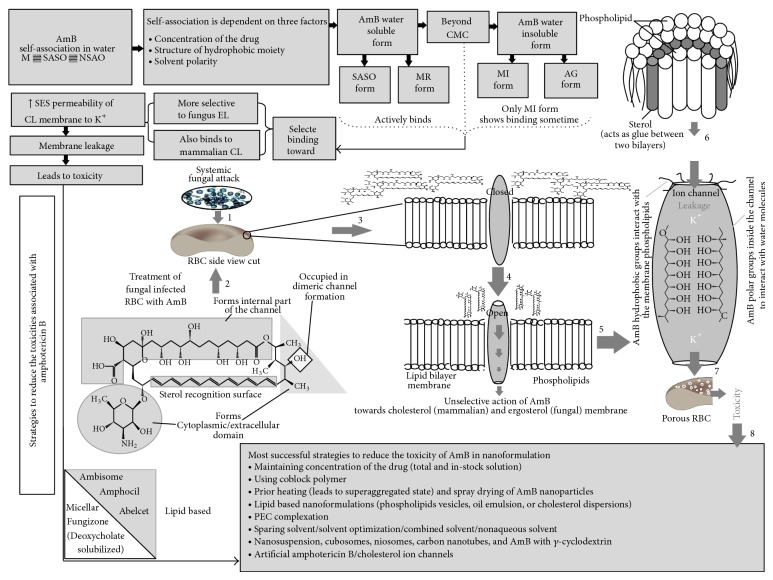
Figure 2.
Mechanism of antifungal action of amphotericin B representing its relation with the nature of arrangement (form) in aqueous state with its associated toxicities and cures. This hypothetical figure demonstrates how association of AmB affects antifungal activity of the whole dug. AmB, oldest drug that does not induce resistance, possesses poor solubility in water (soluble in some organic solvent, e.g., DMSO/DMF) but beyond critical micellar concentration (CMC) AmB starts self-association in aqueous media. This type of association in aqueous media creates the equilibrium stage (between monomers (M), self-associated soluble oligomers (SASO), and nonsoluble aggregation of oligomers (NSAO)) which is dependent on several factors as depicted in Figure 2. Beyond CMC, the solubilized form (monomeric (MR) and self-associated oligomer) is converted into insoluble form aggregated {(AG)/miccellar (MI) form}. Therefore due to availability of several forms of single drug it attains different types of activity. The soluble form can be an active form since it actively binds to the membrane either at once or after reconstitution in micelles within the lipid bilayer but it is only possible beyond CMC. Among insoluble, the micellar form can be active in some cases. As a result the overall activity of AmB is dependent on the equilibrium stage between the different forms present in the aqueous medium. Factors influencing this stage can change the whole activity of the drug. Among these two forms, soluble form (self-associated oligomer) effectively/unselectively binds with the fungal ergosterol membrane and cholesterol membrane by increasing permeability to K+ but proved to be more toxic than aggregated form as it causes leakage to mammalian cholesterol also. This leakage is governed by formation of AmB-sterol complex in a fashion where polar groups head towards the inside of the channel and hydrophobic groups interact with the outside phospholipid membrane. This may lead to various toxicity problems. Nowadays various strategies have been adopted to reduce these toxicities while formulating AmB in nanoform [8–14].