Abstract
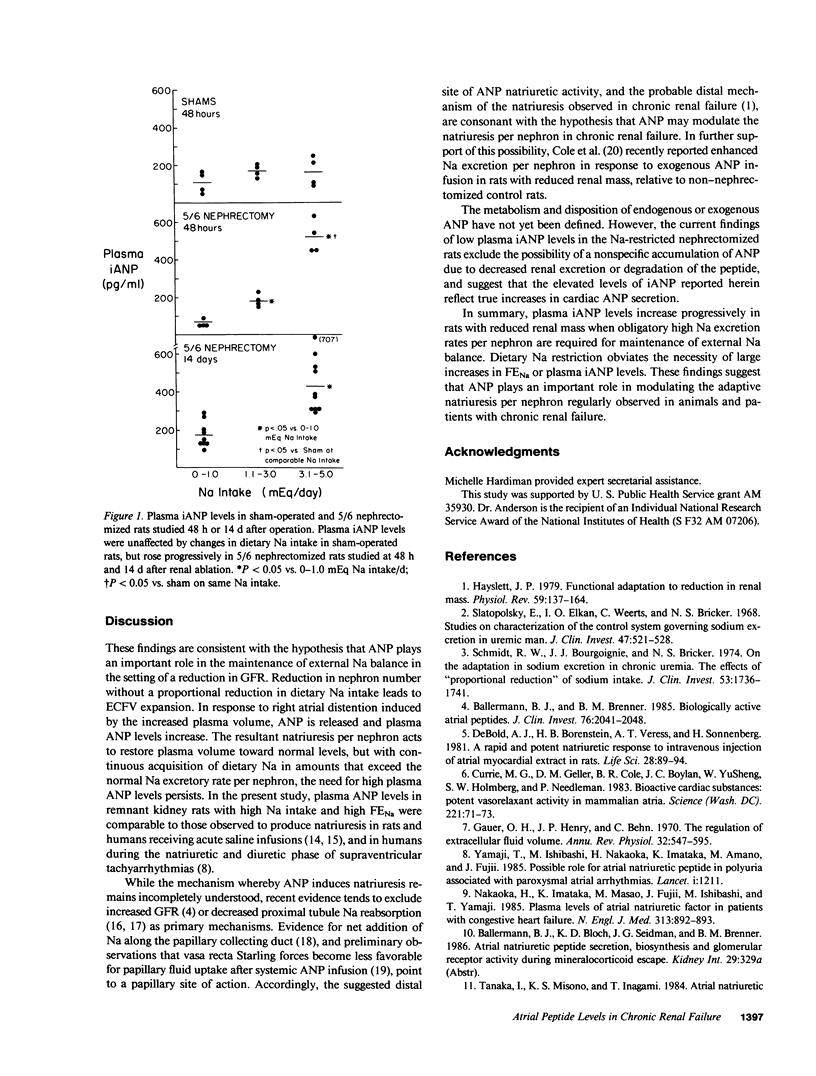
The kidney maintains constancy of body fluid volume by regulating urinary sodium (Na) excretion. In chronic renal failure, the reduction in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is accompanied by an increase in Na excretion per nephron if dietary Na intake is not changed. Reduction in Na intake in proportion to reduced GFR obviates this adaptive increase in tubule Na excretion. To examine the potential role of endogenous atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) in modulating the enhanced Na excretion per nephron in chronic renal failure, we studied rats subjected to 5/6 nephrectomy or sham operation on low, normal, and high Na intakes. Urinary Na excretion increased with increasing dietary Na in all groups, and Na excretion per nephron was increased in 5/6 nephrectomized rats as compared with sham-operated rats on the higher Na intakes. Plasma ANP levels were unaffected by dietary Na manipulations in sham-operated rats, but rose progressively in 5/6 nephrectomized rats with increasing Na intake. Despite extensive nephron reduction, however, plasma ANP levels failed to rise in uremic rats on low Na diets and in this group Na excretion per nephron also failed to rise. We conclude that enhanced ANP secretion may play an important role in promoting the adaptive increase in Na excretion per nephron in chronic renal failure. Restriction of dietary Na in the setting of reduced GFR obviates the stimulation of ANP secretion as well as the adaptive increase in Na excretion rate per nephron.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballerman B. J., Brenner B. M. Biologically active atrial peptides. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2041–2048. doi: 10.1172/JCI112206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. R., Kuhnline M. A., Needleman P. Atriopeptin III. A potent natriuretic, diuretic, and hypotensive agent in rats with chronic renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2413–2415. doi: 10.1172/JCI112254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie M. G., Geller D. M., Cole B. R., Boylan J. G., YuSheng W., Holmberg S. W., Needleman P. Bioactive cardiac substances: potent vasorelaxant activity in mammalian atria. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.6857267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauer O. H., Henry J. P., Behn C. The regulation of extracellular fluid volume. Annu Rev Physiol. 1970;32:547–595. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.002555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayslett J. P. Functional adaptation to reduction in renal mass. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):137–164. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L., Lewicki J., Johnson L. K., Cogan M. G. Renal mechanism of action of rat atrial natriuretic factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):769–773. doi: 10.1172/JCI111759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. E., Thölken H., Ganten D., Luft F. C., Ruskoaho H., Unger T. Atrial natriuretic factor--a circulating hormone stimulated by volume loading. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):264–266. doi: 10.1038/314264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaoka H., Imataka K., Amano M., Fujii J., Ishibashi M., Yamaji T. Plasma levels of atrial natriuretic factor in patients with congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 3;313(14):892–893. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510033131416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. W., Bourgoignie J. J., Bricker N. S. On the adaptation in sodium excretion in chronic uremia. The effects of "proportional reduction" of sodium intake. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1736–1741. doi: 10.1172/JCI107725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatopolsky E., Elkan I. O., Weerts C., Bricker N. S. Studies on the characteristics of the control system governing sodium excretion in uremic man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):521–530. doi: 10.1172/JCI105748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H., Cupples W. A., de Bold A. J., Veress A. T. Intrarenal localization of the natriuretic effect of cardiac atrial extract. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;60(9):1149–1152. doi: 10.1139/y82-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka I., Misono K. S., Inagami T. Atrial natriuretic factor in rat hypothalamus, atria and plasma: determination by specific radioimmunoassay. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):663–668. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91606-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaji T., Ishibashi M., Nakaoka H., Imataka K., Amano M., Fujii J. Possible role for atrial natriuretic peptide in polyuria associated with paroxysmal atrial arrhythmias. Lancet. 1985 May 25;1(8439):1211–1211. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92883-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J., Borenstein H. B., Veress A. T., Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 5;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


