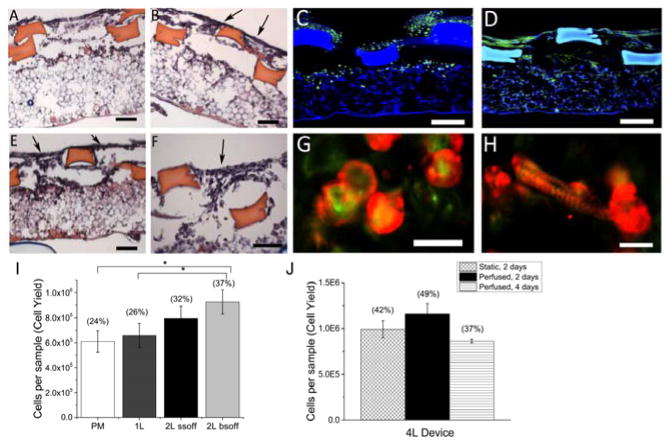
Figure 4.
Heart cell scaffolds support cell attachment and elongation. (A,B,E,F) Distributions of heart cells cultured statically for 2 days on (A) 2L SSoff plus PM or (B,E,F) 2L BSoff plus PM scaffolds in H&E stained cross-sections taken either perpendicular (A,B) or parallel (E,F) to the long axis of the rectangular pores. Arrows (B,E,F) show gaps between struts. Scale bars 100 μm. (C,D,G,H) Morphologies of heart cells cultured statically for (C,G) 2 days or (D,H) 4 days in confocal micrographs after staining for (C,D) actin (green) or co-staining for (G,H) actin (green) and sarcomeric-α-actinin (red). Scale bars (C,D) 100 μm; (G,H) 20 μm. (I) Cell delivery capacities of 0.2 square cm scaffolds with four architectures, PM, 1L plus PM, 2L SSoff plus PM, and 2L BSoff plus PM, after two days of static culture; (J) Cell delivery capacities of 0.2 square cm scaffolds punched from 4 square cm 4L devices and cultured statically or with perfusion for 2 or 4 days. Data show Average +/− SE; parentheses indicate corresponding cell seeding yields (%). *Significantly lower than 2L BSoff plus PM. (Table S2).