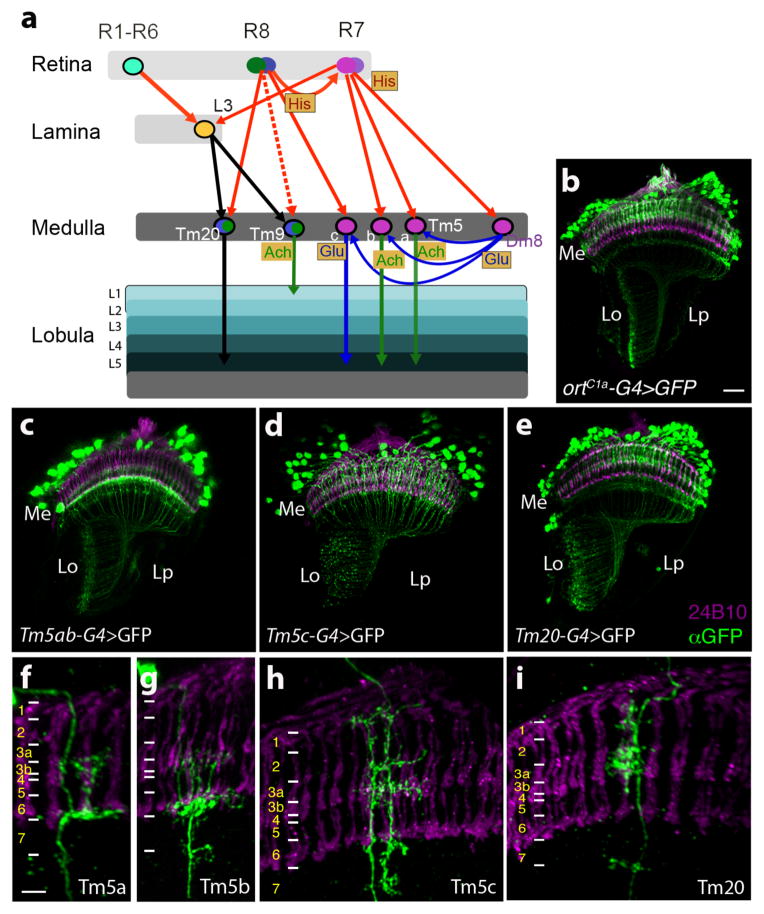
Figure 4. Visual circuits downstream of chromatic photoreceptors.
(a) Schematic of currently known visual circuits, highlighting the neurons known to receive input from multiple photoreceptors. Neuronal cell bodies are denoted by ovals. Arrows indicate axonal projections, a solid arrow between two neurons indicates a chemical synapse validated by electron microscopy, a dashed arrow indicates a chemical synapse determined using GRASP (GFP Reconstitution Across Synaptic Partners; Feinberg et al.,2007; Gordon and Scott, 2009; Karuppudurai et al., 2014). Arrows are color coded according to the neurotransmitter system expressed in the particular neuronal type. Thus, histaminergic projections from the photoreceptors are red, glutamatergic projections are blue, cholinergic projections are green, and axonal projections of an undetermined neurotransmitter type are black. Neurotransmitter systems expressed in particular cell types are also marked in shaded boxes. Ach: Acetylcholine, Glu: Glutamate, His: Histamine.
(b–i) Confocal images of adult optic lobes stained with mAb24B10 (magenta) to label photoreceptors and therefore mark medulla column positions, and an anti-GFP antibody to mark target neuron projections. (b) ortC1a-GAL4>UASmCD8GFP. (c–e) ortC1a-GAL4 DBD crossed to different dVP16AD lines to generate subtype-specific lines. (c) ortC1a-GAL4DBD; 24g-dVP16AD. Single cell flip out clones identify labeled cells in this line as Tm5a (f), and TM5b (g). (d) ortC1a-GAL4DBD/OK371-dVP16AD. Single cell flip out clones indicate that this driver combination labels largely Tm5c neurons (h). (e) ortC1a-GAL4 DBD/ET9A-dVP16AD. Single cell flip out clones indicate that this driver combination labels largely Tm20 neurons (i). Scale bars: 20 μm in b for c-e; 5 μm in f for g-i. Positions of medulla layers are marked in f-i.