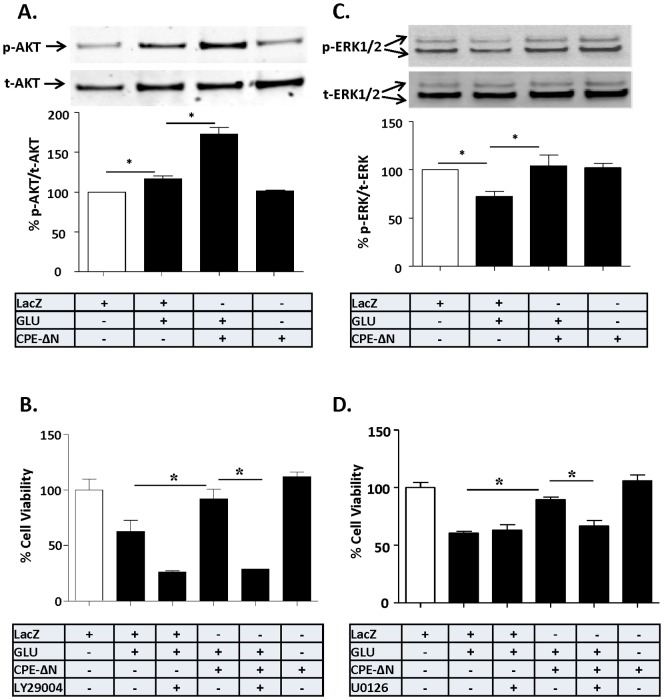
Figure 5. Neuroprotection by CPE-ΔN involves AKT and ERK signaling pathways.
In A–D, rat primary cortical neurons were transduced with CPE-ΔN or LacZ vectors and subsequently challenged with or without glutamate for 24 h. A. Top panel: Western blot analysis of p-AKT protein in cortical neurons. Actin was also analyzed and served as an internal control for protein load. Bottom panel: Bar graphs showing the quantification of p-AKT normalized to t-AKT and expressed as a % compared to vehicle treated control cells. Note that CPE-ΔN significantly increased the level of p-AKT after the glutamate treatment in primary cultured cortical neurons. At least three independent experiments were done. Data shown represent all the experiments combined. B. Bar graphs showing WST activity, indicative of cell viability, of cortical neurons treated with and without glutamate in the continued presence or absence AKT inhibitor, LY294002. Note the neuroprotective effect of CPE-ΔN was completely blocked by LY294002, suggesting the AKT signaling pathway is involved in the neuroprotective effect of CPE-ΔN in primary cortical neurons. Two independent experiments were done. Data shown represent one experiment. C. Top panel: Western blot analysis of p-ERK in primary cortical neurons. Actin was also analyzed and served as an internal control for protein load; bottom panel: Bar graphs showing the quantification of p-ERK normalized to t-ERK and expressed as a % compared to vehicle treated control cells. Note that CPE-ΔN significantly inhibited the glutamate-induced decrease in p-ERK in primary cortical neurons. At least three independent experiments were done. Data shown represent all the experiments combined. D. Bar graphs showing WST activity, indicative of cell viability of cortical neurons treated with and without glutamate in the continued presence or absence of the ERK inhibitor, U0126. Note the neuroprotective effect of CPE-ΔN was partially blocked by U0126 suggesting the involvement of ERK signaling pathway in the cortical neurons. Two independent experiments were done. Data shown represent one experiment. n = 4/group (A); 5/group (B); 4/group (C); 5/group (D). Values are mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test, *p<0.05.