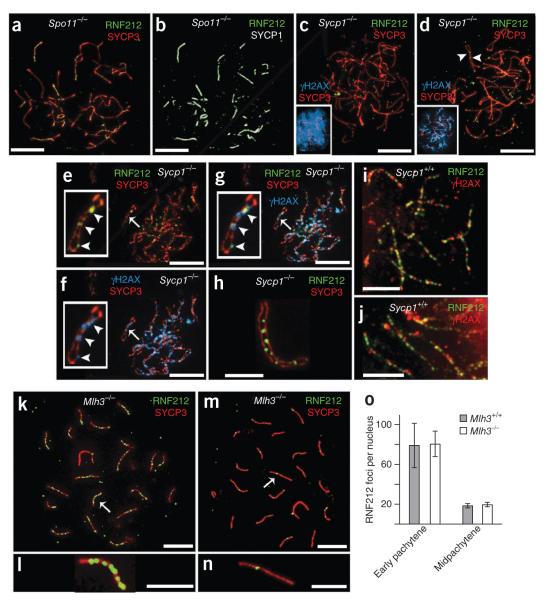
Figure 2.
Genetic requirements for RNF212 localization. (a,b) Spermatocyte nucleus from a Spo11−/− mouse with immunolabeling for SYCP3 and SYCP1 (a) and RNF212 and SYCP1 (b). (c–g) Spermatocyte nuclei from a Sycp1−/− mutant mouse immunolabeled for RNF212, SYCP3 and γH2AX. (c) Zygotene-like nucleus with pannuclear γH2AX staining. (d) Pachytene-like nucleus with diminishing γH2AX staining. Insets in c and d show SYCP3 and γH2AX channels. Arrowheads in d highlight RNF212 foci localized to coaligned homolog axes. (e–g) Late-pachytene/early diplotene nucleus stained for RNF212 and SYCP3 (e) and γH2AX and SYCP3, showing residual γH2AX foci (f). (g) Merged staining of this nucleus for RNF212, SYCP3 and γH2AX. Insets in e–g show a single homolog pair, with RNF212-γH2AX foci highlighted by arrowheads. (h) Selected homolog pair from a Sycp1−/− spermatocyte showing RNF212 foci associated with one of the two SYCP3-staining axes. (i) Representative homolog pairs from a wild-type early pachytene spermatocyte immunolabeled for RNF212 and γH2AX. (j) Independent nucleus immunolabeled as in i. (k–n) Spermatocyte nuclei from an Mlh3−/− knockout mouse, immunolabeled for RNF212 and SYCP3. (k,l) Early pachynema nucleus (k), with magnified view of the chromosome indicated by an arrow (l). (m,n) Midpachynema nucleus (m), with magnified view of the indicated chromosome (n). (o) Quantification of RNF212 foci (± s.d.) in early pachytene and midpachytene spermatocytes from wild-type and Mlh3−/− mice. For wild-type cells, 16 early pachytene and 16 midpachytene nuclei were analyzed. For Mlh3−/− cells, 39 early pachytene and 10 midpachytene nuclei were analyzed. Scale bars, 10 μm in a–g,k,m and 5 μm in h–j,i,n.