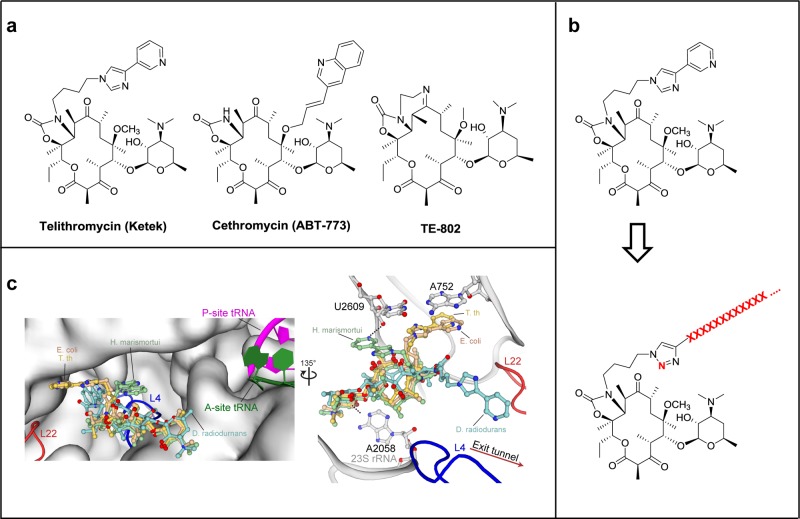
Figure 1.
Design of peptide–ketolide (peptolide) compounds. (a) Structures of representative ketolides: telithromycin (TEL), cethromycin, and TE-802. (b) Binding of TEL to the 50S subunit of the ribosome. (Left) An overlay of TEL shows alternate positioning of the alkyl-aryl arm when bound to T. thermophilus (yellow, PDB ID 3OI3), E. coli (beige, PDB ID 3OAT), H. marismortui (green, PDB ID 1YIJ), and D. radiodurans (cyan, PDB ID 1P9X). TEL binds to the 50S exit tunnel in between the PTC, represented by the P-site and A-site tRNA, and the constriction site in the exit tunnel formed by 50S ribosomal protein L4 (blue) and L22 (red). (Right) In each of the macrolide structures, the desosamine sugar hydrogen bonds with A2058 stabilizing the macrolactone ring. The alkyl-aryl arm stacks against the A752:U2609 base pair in T. thermophilus (yellow) and E. coli (beige). In the absence of the A752:U2609, the alkyl-aryl arm hydrogen bonds to U2609 in H. marismortui (green) or extends down the exit tunnel in D. radiodurans (cyan). There is a 135° orientation between the left and right panel. (c) General structure of peptolide derived from TEL. Changes to the TEL template to yield the target peptolide probes are highlighted in red with ···XXXX··· indicating polypeptide containing any combination of amino acids of interest.