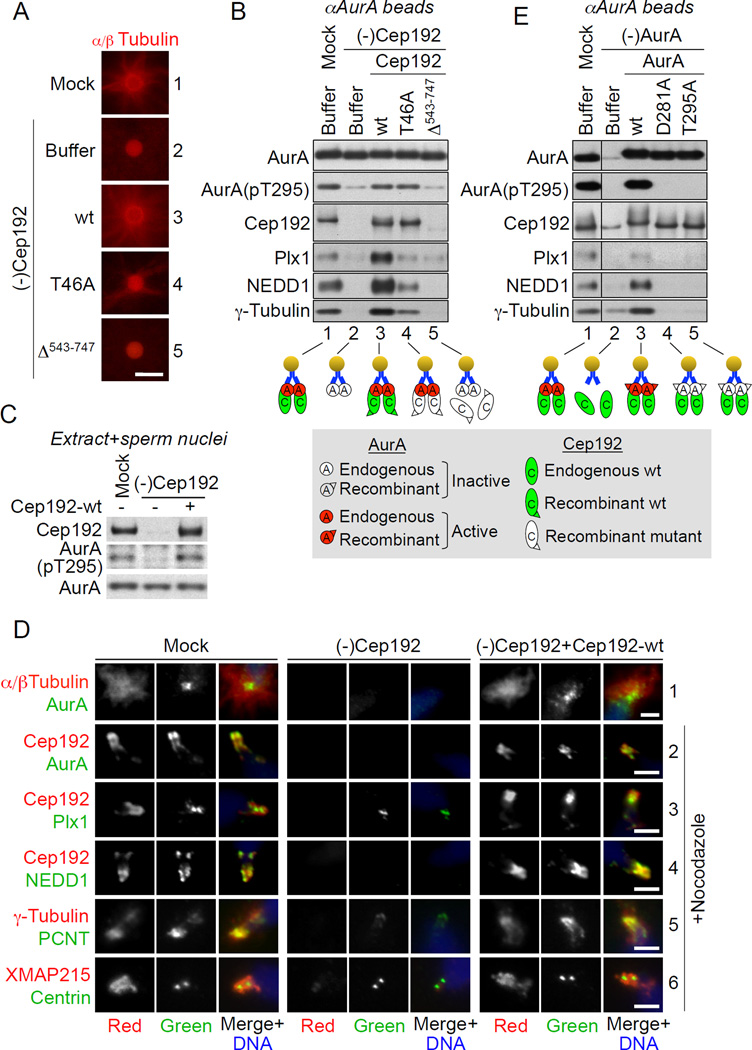
Figure 1. Cep192, in a complex with active AurA, recruits multiple PCM proteins.
(A) Fluorescence microscopy of αAurA beads incubated in mock-treated and Cep192-depleted [(-)Cep192] extracts supplemented with rhodamine tubulin and with extract buffer (XB) or the indicated recombinant full-length Cep192 proteins. Scale bar, 5 µm.
(B) Western blot (W-blot) of aAurA beads retrieved from nocodazole-supplemented extracts treated as in (A). Cep192-T46A and Cep192-Δ543–747 are Cep192 mutants lacking the Plx1-docking threonine 46 and the AurA-BD, respectively.
(C) W-blot of M-phase mock-treated and Cep192-depleted extracts supplemented with XB or recombinant full-length Cep192-wt and with sperm nuclei.
(D) Immunofluorescence (IF) of sperm centrioles in extracts treated as in (C) in the absence/presence of nocodazole. Scale bars, 2.5 µm.
(E) W-blot of aAurA beads incubated in mock-treated and AurA-depleted extracts supplemented with XB or the indicated AurA proteins. AurA depletion was performed using a bead-immobilized AurA-binding Cep192 fragment (Cep192521–757), instead of αAurA beads, to prevent co-depletion of endogenous Cep192.
In (B) and (E), the lower panels schematically illustrate bead-protein interactions. W-blots of extracts used in these experiments are shown in Figures S1C and S1D.
See also Figure S1.