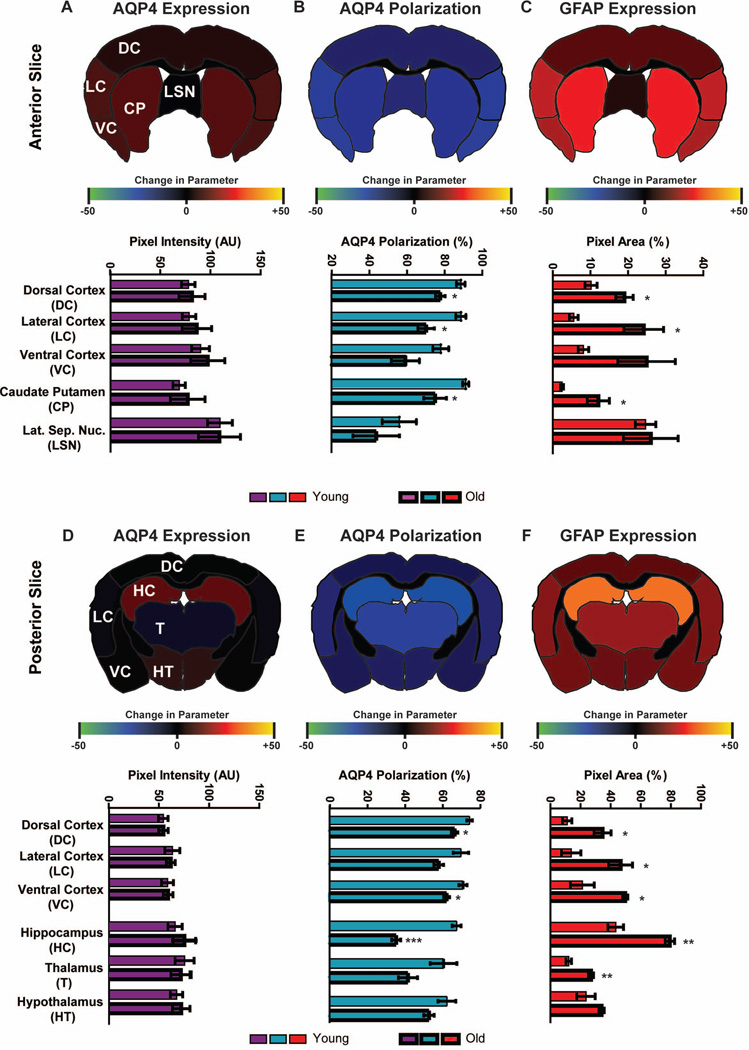
Figure 6. Impairment of perivascular AQP4 polarization is greatest in the lateral and ventral cortex, hippocampus and striatum of the aging brain.
AQP4 expression and polarization and GFAP expression were evaluated by immunofluorescence in fixed brain slices from young (2–3 month) and old (18 month) brains. Expression and polarization were evaluated within different regions of anterior (A-C) and posterior (D-F) brain slices. Regional heat maps depict mean change in AQP4 expression (AQP4 immunofluorescence), AQP4 polarization (% area), and GFAP expression (% area) between young and old brains. (A, D) Within both the anterior and posterior regions, global AQP4 immunofluorescence did not differ between the young and old brains. (B, E) Perivascular AQP4 polarization was significantly reduced in the aged brain, with most pronounced effects in the lateral and ventral cortex, striatum and hippocampus (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***<0.001, Young vs. Old; 2-way ANOVA; n = 4 per group). (C, F) GFAP expression was significantly increased in the old compared to the young brain, with the greatest effect evident within the lateral and ventral cortex, hippocampus and striatum (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***<0.001, Young vs. Old; 2-way ANOVA; n = 4 per group).