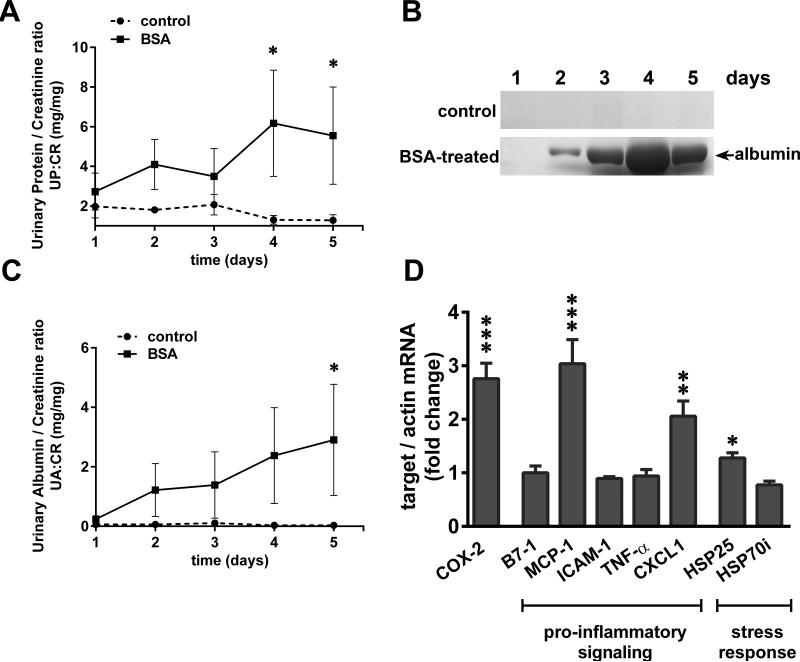
Figure 1.
SA-overload in rats induces proteinuria and glomerular expression of COX-2, pro-inflammatory and stress genes. A) Urinary protein/creatinine ratios (UP:CR) of the BSA-treated rats vs control rats (n=3 for each group; *P<0.05 versus control, determined by two way ANOVA Tukey's multiple comparisons test). B) Massive amounts of urinary albumin are excreted from BSA-treated rats but not control rats (representative gels are shown from each group). Urine was collected on five consecutive days and equal volumes (4 μl) analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. C) Urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (UA:CR) of the BSA-treated rats vs control rats (n=3 for each group; *P<0.05 versus control, determined by two way ANOVA Tukey's multiple comparisons test). D) Total RNA was extracted from the isolated glomeruli of control and BSA-treated rats and relative mRNA levels of COX-2, pro-inflammatory and stress genes were measured by qRT-PCR and normalized to β-actin (*P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 versus control, determined by t test).