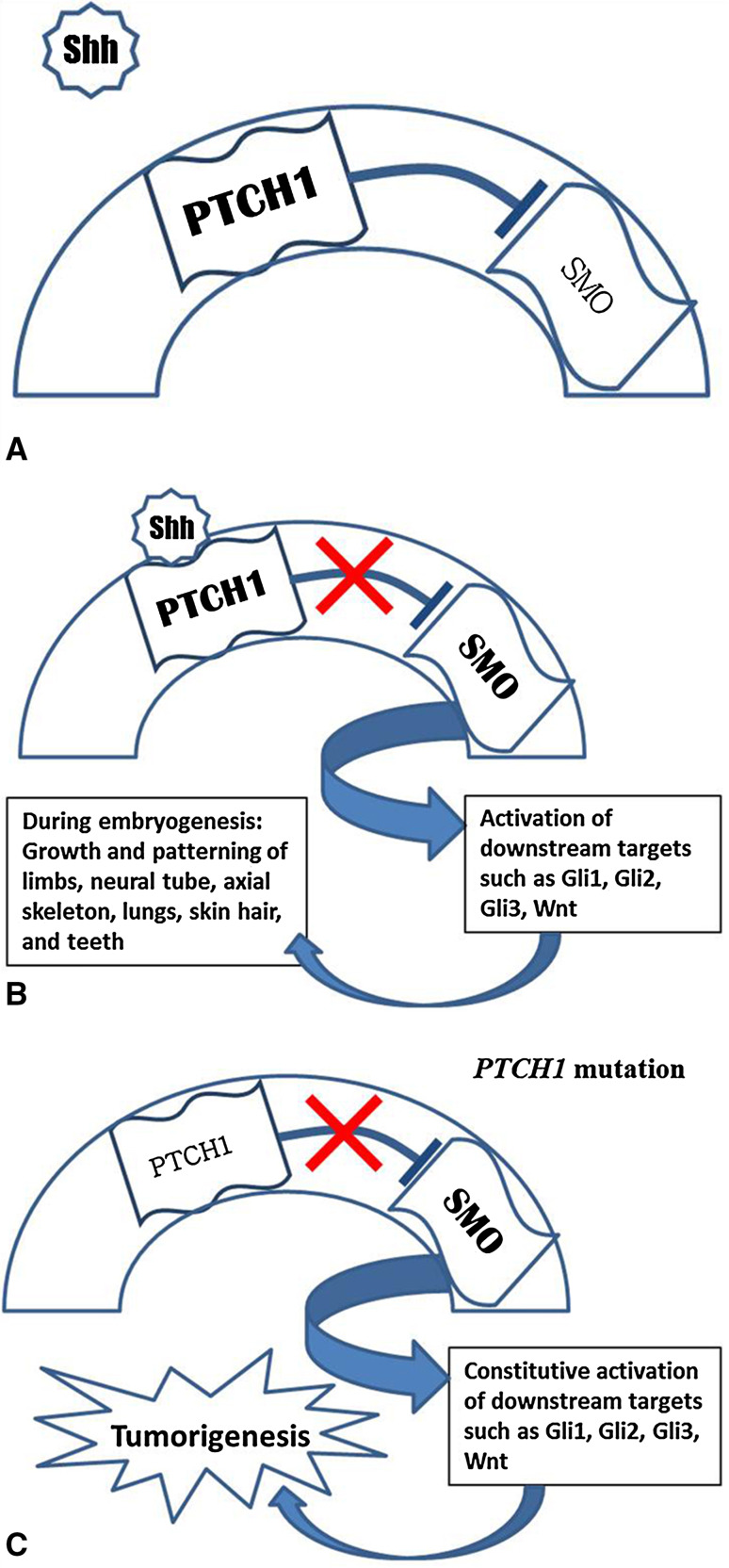
Fig. 3.
a PTCH1 is a transmembrane receptor which inhibits SMO in the absence of Shh. b Binding of Shh to PTCH1 releases the inhibitory effect on SMO, activating the Shh pathway and associated downstream targets. During embryogenesis, this leads to growth and patterning of the limbs and of various tissues. c Mutation of PTCH1 results in loss of SMO inhibition. Tumorigenesis appears to result from constitutive activation of Shh-related proteins such as Gli1, Gli2, Gli3, and Wnt