Figure 5.
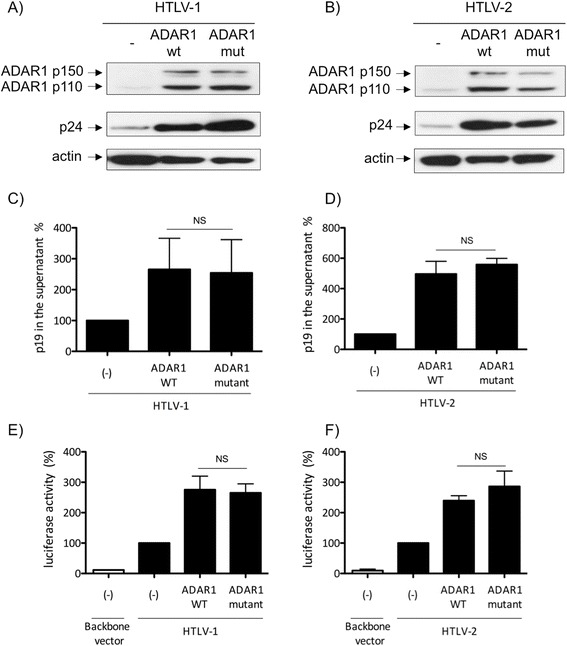
ADAR1 enhances HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 replication independently from its editing activity. 293-T cells were transfected with (A, C) 4 μg of pACH or (B, D) pH6neo molecular clones together with 500 ng of a plasmid coding for ADAR1 wild-type or for an editing-deficient ADAR1 protein (ADAR1 mutant). (A, B): Western blot analyses were performed on 60 μg of proteins obtained from whole cell extracts using anti-p24gag, anti-ADAR1 and anti-actin antibodies. (C, D): p19gag was quantified in supernatant obtained from cells transfected as in (A, B). Data are represented as fold change compared to the p19gag values obtained for cells that were not transfected with the ADAR1 plasmid arbitrarily set to 100%. (E, F): Jurkat cells were transfected with 2 μg of (E) pACH or (F) pH6neo molecular clones, together with 1 μg of a plasmid encoding either ADAR1 wild-type or ADAR1 mutant and 2 μg of (E) HTLV-1-LTR or (F) HTLV-2-LTR-luc plasmid. Forty-eight hours later, luciferase activity was measured and results normalized to protein concentration as determined by the Bradford method and calculated as fold change compared to cells non transfected with ADAR1 plasmid arbitrarily set to 100%. (C-F): Data are the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from 3 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between treated and untreated cells (paired Student t test; NS: non significant).
