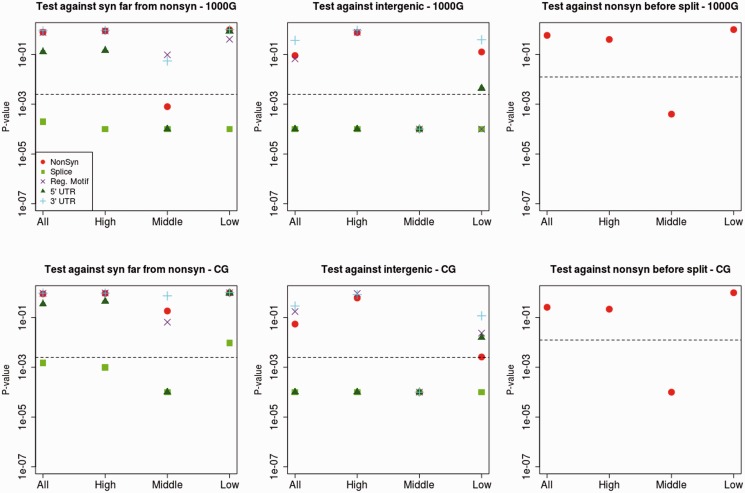
Fig. 2.
P values from bootstrap-based test (Hernandez et al. 2011) comparing various genomic classes to look for significant differences in modern human diversity per site scaled by divergence to the human–chimpanzee ancestor in a 0.02-cM region around modern-human-specific changes. We tested putatively functional categories (nonsynonymous, splice site and UTR changes) against putatively neutral categories: 1) Synonymous changes far from any nonsynonymous change (left panels) and 2) intergenic changes (middle panels). We also compared nonsynonymous modern-specific changes against nonsynonymous changes that fixed before the modern-Neandertal human population split (right panels). The top panels were produced using the 1000 Genomes Project (1000G) data and the bottom panels were produced using the CG data. The x axis denotes the partitioning of scaled diversity values into quantiles (all sites, highest third, middle third, and lowest third) in each of the two categories under comparison. Black dashed lines denote the Bonferroni-corrected P values (0.05/20 = 0.0025 for left and middle panels; 0.02/4 = 0.0125 for right panels).