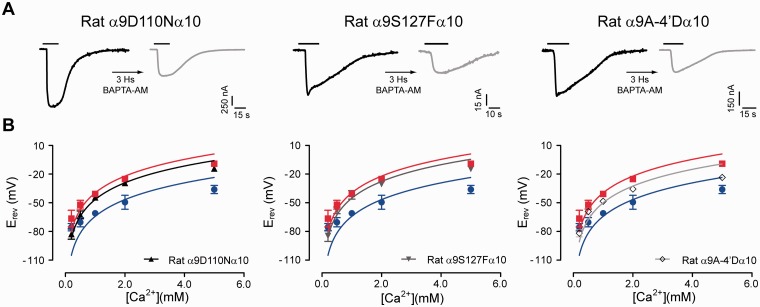
Fig. 5.
Mutations in the extracellular vestibule and the exit of the channel pore alter calcium permeability of the rat α9α10 receptor. (A) Representative traces of responses evoked by 100 μM ACh in oocytes expressing rat α9α10 single mutant receptors: rat α9D110Nα10 (left panel), rat α9S127Fα10 (middle panel), and rat α9 A-4′Dα10 (right panel), before (left—black trace) and after (right—gray trace) a 3-h incubation with the fast calcium chelator BAPTA-AM (Vhold = −70 mV; [Ca2+]extracellular = 1.8 mM). Traces are representative of n = 4–6 per group. (B) Plot of Erev values as a function of extracellular Ca2+ concentration for rat α9D110Nα10 (left panel), rat α9S127Fα10 (middle panel), and rat α9 A-4′Dα10 (right panel) single mutant receptors. Erev values for rat α9α10 (red) and chicken α9α10 (blue) are shown for comparison. Values are mean ± SEM of 5–11 experiments per group. Solid lines are fit to the GHK equation (see Materials and Methods).