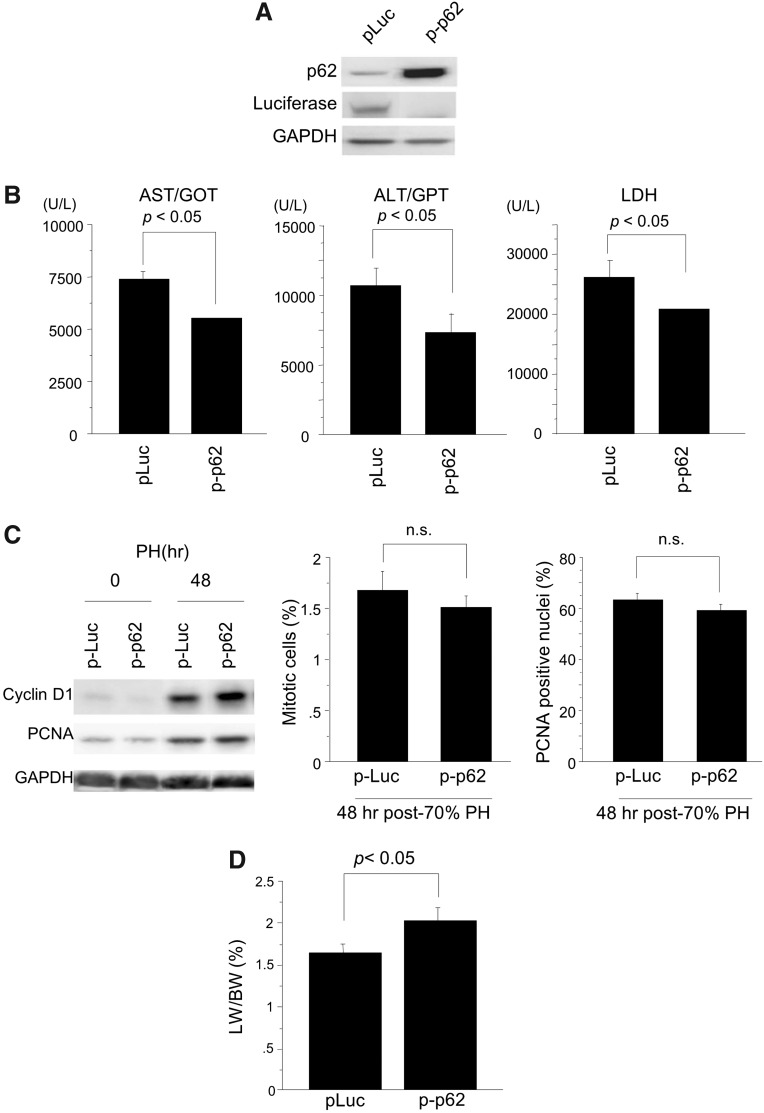
FIG. 7.
Hepatic transduction of the p62/SQSTM1 gene markedly reduces post-PH liver injury and improves regeneration of the steatotic liver of db/db mice. Post-PH liver injury and regeneration were evaluated in db/db mouse liver transduced with the p62/SQSTM1 gene. (A) Western blot analysis shows the robust induction of p62/SQSTM1 protein in the liver of db/db mice by hydrodynamic injection of the p62/SQSTM1 gene (p-p62). Plasmid DNA of luciferase gene was injected as a control (p-Luc). (B) Serum levels of AST, ALT, and LDH were reduced at 12 h post-PH in the p62/SQSTM1-transduced steatotic liver, as compared with the luciferase-transduced control liver. (C) Expression of PCNA and cyclinD1 protein peaked at 48 h post-PH similarly in both the control and p62/SQSTM1-expressing liver; in addition, there was no significant difference in the mitotic index and the counts of PCNA-positive hepatocytes between the two types of liver. (D) Liver regeneration recovered partially, but not completely, after transduction of p62/SQSTM1 into the steatotic liver. At least five mice were used for each experiment. Data are expressed as mean±SEM; p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase.