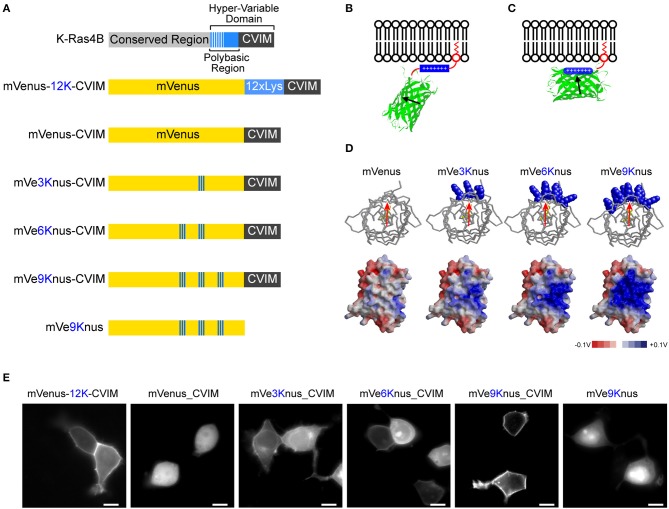
Figure 1.
Engineering of mVe9Knus-CVIM. (A) Primary structures of K-ras4B as well as the six mVenus-based constructs studied. “CVIM” in the gray box represents the farnesylation signal. The engineered lysine resides in mVenus-based constructs are highlighted in blue. (B,C) The design of these constructs consists in transferring the polybasic region to the surface of mVenus, aiming to orient it in a geometrically defined manner at the membrane-cytoplasm interface. (D) Top: Top views of mVenus and the three mutant models. The introduced lysine residues are highlighted in the blue, space-filled models. The red arrow approximates the transition dipole moment. Bottom: Side views of electrostatic surface potential maps in these models. (E) Representative images of HEK293 cells expressing the corresponding constructs. Bars = 10 μm.