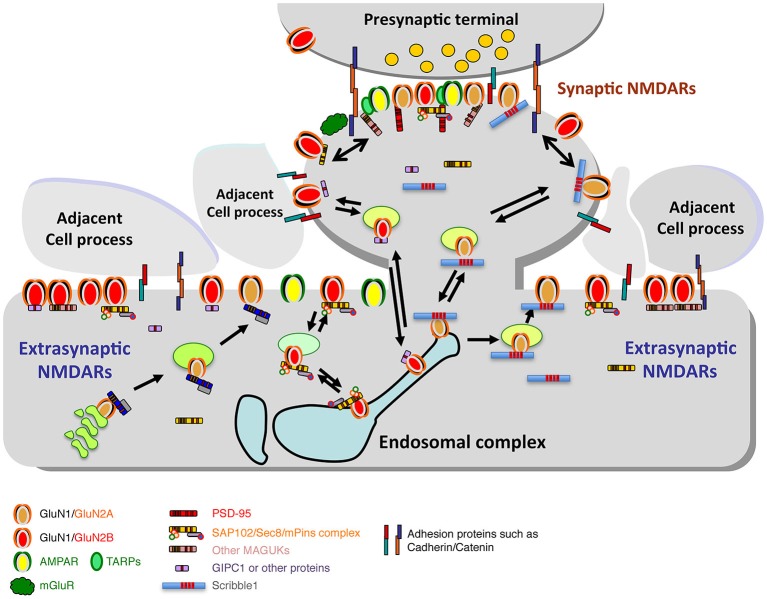
Figure 4.
Diagram illustrating the synaptic and extrasynaptic distributions of NMDARs and associated scaffolding and adhesion proteins, and especially the associations of extrasynaptic NMDARs with adjacent cell processes. Note that other GluRs (AMPARs, kainate and delta iGluRs, and metabotropic GluRs (mGluRs)) are found at synapses and in extrasynaptic locations. AMPARs are typically the most abundant GluRs at synapses and may also be more common than NMDARs in extrasynaptic locations in some neurons. mGluRs are also widespread; some forms are particularly abundant in the perisynaptic zone. Like NMDARs, these GluRs also show close associations with other proteins that affect their trafficking and localization (not illustrated here). Trafficking of NMDARs through the Golgi pathway and/or endosomes is mediated by a number of associated proteins such as MAGUKs and Scribble1 (see text for details). Diagram and legend text is modified from Figure 4 of Petralia, 2012.