Figure 1.
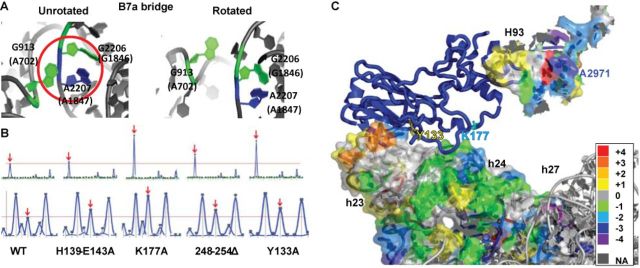
uL2 B7b bridge mutants alter the rotational equilibrium of the ribosome. (A) The B7a intersubunit bridge. In the nonrotated ribosome, A2207 (25S rRNA) and G913 (18S rRNA) engage in a triple-base interaction along with G2206. In the rotated state, the base triple is disrupted, and the 2′ OH-group on A2207 becomes accessible to modification by 1M7. Similarly, atoms on G913 become accessible to modification by kethoxal upon rotation. Images were generated in PyMOL using atomic and near atomic resolution yeast ribosomal structures (13,45). Escherichia coli base numbers are shown in parentheses. (B) Reactivity peaks obtained by hSHAPE after chemical probing of the landmark base G913 (arrows) at the SSU side of the B7a intersubunit bridge with kethoxal (upper panel) and probing of the landmark base A2207 (arrows) at the LSU side of the B7a intersubunit bridge with 1M7 (lower panel). (C) Differences in 1M7 reactivity between uL2-K177A and WT 18S and 25S rRNA regions probed by hSHAPE. The reactivity differences were assigned color codes according to the scale shown to the right. Warmer colors indicate increased reactivity and cooler colors denote decreased reactivity. Scored data were mapped on 3.0 Å resolution yeast ribosomes (13) using PyMOL.
